User:DJ Cane/sandbox2
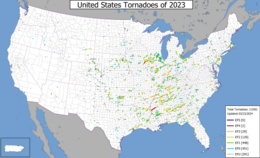 A map of 2023 United States tornado paths from the results of preliminary surveys. | |
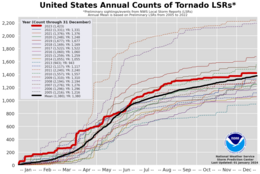 A chart of the 2023 United States tornado local storm report count compared to years 2005 through 2022, and the 2005–2022 mean. | |
| Timespan | January 2–ongoing |
|---|---|
| Maximum rated tornado | EF4 tornado
|
| Tornadoes in U.S. | 1,267 |
| Damage (U.S.) | > $1.099 Billion[1] |
| Fatalities (U.S.) | 82 |
| Fatalities (worldwide) | 115 |
This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2023. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail.
There have been 1,310 preliminary filtered reported tornadoes[2] and 1,267 confirmed tornadoes in the United States in 2023. At least 125 other tornadoes have touched down outside of the United States as well. Worldwide, 115 tornado-related deaths have been confirmed, 82 of them in the United States, 12 in China, nine in Indonesia, eight in Myanmar, three in Turkey, and one in Saudi Arabia.
January saw the third-highest number of tornado watches and confirmed tornadoes of any January on record in the United States.[3] Additionally, the first two months of the year saw the fourth-highest number of confirmed tornadoes for the first 59 days of any year on record.[4] In addition, the year has been deadlier than average, with multiple fatal tornadoes. By April 5, 63 deaths from tornadoes had been recorded in the United States; this was almost three times higher than 2022's total of 23 deaths and approaching the annual average of roughly 70 deaths.[5] Although below average tornadic activity occurred in May, active weather patterns consistently spawned damaging tornado outbreaks throughout the summer, causing 12 additional fatalities. Multiple damaging tornadoes also affected portions of Canada during that time, including the first violent tornado in the country since 2018. However, tornadic activity decreased dramatically in September and was almost non-existent through a large portion of the autumn months. This was mostly due to most Atlantic tropical cyclones missing the United States during the peak of hurricane season and few early-season frontal systems.
Notably this year, several organizations across Europe including the European Severe Storms Laboratory and Deutscher Wetterdienst published and began using the new International Fujita scale, starting in August 2023.[6] The first major tornado outbreak to use that scale occurred three months later when European windstorm Storm Ciarán affected a large portion of Europe.
Africa
[edit]This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2023) |
Asia
[edit]China
[edit]April 15
[edit]A tornado struck areas near the large city of Linyi, Shandong Province, with significant damage observed in the Tancheng County village of Lizhuangzhen. The tornado was captured on video from multiple angles, some from close range. Homes and other structures were severely damaged, including some that sustained loss of roofs and exterior walls, while tractors and cars were tossed. Metal truss transmission towers, power poles, and masonry fences were toppled over, and outbuilding structures were destroyed as well. Trees were snapped, and several people were injured. Another tornado was reported in northern Shandong Province as well. Neither of the tornadoes were officially rated.[7][8][9][10]
June 1
[edit]Multiple tornadoes impacted parts of Liaoning Province in northeastern China on June 1. A destructive tornado moved through parts of Fuxin City and areas outside outside of the city, heavily damaging or destroying at least 60 homes. Multiple apartment buildings and other structures were also heavily damaged, and buildings were destroyed at a coal mine as well. Cars and tractors were tossed and damaged, and trees and power lines were downed along the path. No fatalities were reported, but 13 people were injured.[11][12] A narrow but significant tornado impacted farms and rural areas outside of Kaiyuan, destroying homes and outbuildings, snapping trees, and scouring crops from fields.[13] Kaiyan had previously been hit by a violent EF4 tornado in July of 2019. A third tornado occurred in the Shenyang area, and a fourth was confirmed near Huludao. None of the tornadoes received official intensity ratings.[14][15][16]
July 17
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2023) |
An EF2 tornado struck parts spawned by Severe Tropical Storm Talim of the Chinese city of Danzhou.[17]
August 13
[edit]A deadly EF2 tornado struck parts of Yancheng City, Jiangsu. Approximately 283 residences were damaged or destroyed, two people were reported to have been killed, and at least 15 people were injured.[18][19][20]
September 19
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Two tornadoes moved directly into the city of Suqian, Jiangsu, killing five people and injuring another four.[21] Approximately 1,600 houses were either damaged or completely destroyed. Another tornado struck parts of Funing, Jiangsu, also causing five deaths and four minor injuries.[22] The two tornadoes in Suqian were rated EF2, while the tornado in Funing received an EF3 rating.[23][24]
India
[edit]A large and photogenic cone tornado struck Fazilka in India on March 24, resulting in significant damage. At least 50 unreinforced masonry homes were severely damaged or completely destroyed. Farming equipment was tossed, trees were snapped or uprooted, power poles were downed, and significant crop damage occurred in farm fields. No fatalities occurred, though at least 12 people were injured.[25][26][27]
Indonesia
[edit]A significant tornado struck four different villages in the Kodi District, Southwest Sumba at 2:30 pm Central Indonesian Time (6:30 am UTC). It damaged or destroyed 21 homes in total, killing nine people.[28][29]
Mynamar
[edit]At around 6:10 p.m. on April 21, a strong tornado struck Central Myanmar in Leiway Township near the capital city of Naypyitaw, causing major damage and multiple fatalities in the villages of Tada Oo and Aung Myin Kone. A total of 232 homes were destroyed, and many trees and power lines were downed. A small clinic and two Buddhist monasteries were also destroyed. Eight people were killed and another 128 were hospitalized as a result of the tornado.[30][31]
Oman
[edit]On April 22, a tornado was caught on video by local residents as it struck Jalan Bani Bu Ali in Ash Sharqiyah South Governorate in eastern Oman. The tornado damaged many homes, killed farm animals, and injured a woman. The storm system that spawned the tornado also resulted in torrential rainfall and flash flooding. On the following day, Jalan Bani Bu Ali was hit by another tornado.[32][33]
Saudi Arabia
[edit]A large dusty tornado caused significant damage as it touched down near the outskirts of Taif, Saudi Arabia on March 13, resulting in one fatality. A few buildings sustained major damage, including loss of roofs and exterior walls. Power poles and iron fence posts were knocked over, while cars and trucks were thrown and severely damaged. A man was killed by flying debris, and at least one person was severely injured.[34][35]
Turkey
[edit]April 10
[edit]On April 10 a small outbreak occurred in the Greater Mediterranean. The most significant tornado touched down in the Ağaçören District of Aksaray Province in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. It tracked through or near the villages of Camili, Avşar, Kırımini and Göllü along a 22 km-path (14 mi) with a maximum width of 200 m (220 yd). The tornado, which was rated F2, destroyed the roofs of homes, partially collapsed walls, and killed farm animals. Masonry outbuildings were destroyed, a tractor-trailer was overturned, while trees and power line pylons were downed as well. The minaret tower at the Göllü mosque collapsed, injuring a 26-year-old man. A separate F1 tornado also struck areas in and around Budak, where another mosque also sustained collapse of its minaret tower, outbuildings were destroyed at dairy farms, and some homes had roof damage.[36]
April 20
[edit]| FU | F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Two tornadoes caused damage in Turkey on April 20. The first tornado struck the outskirts of Pazarcık, Kahramanmaraş, where roofing was torn from buildings, cars and storage containers were flipped, and trees were downed. The tornado also struck a camp where people affected by the 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquake were housed, where tents were torn apart and struck by flying debris. Three people were killed at the camp and 150 others were injured. The tornado was rated F1 on the Fujita scale by the European Severe Storms Laboratory. A second F1 tornado struck the village of Tatlıçayır, Diyarbakır Province, where homes sustained roof damage, a frail masonry outbuilding was destroyed, trees were downed, and farm animals were injured.[36]
May 6
[edit]An F2 tornado caused damage in the Sultan Alaaddin, Akarca and Ören districts as it moved through the city of Anamur, Turkey. Homes and apartment buildings sustained damage to their roofs, windows, and balconies, and some businesses were also damaged. Vehicles were flipped and tossed, and trees and power lines were downed as well. Around 100 large commercial greenhouses were damaged or destroyed, and 13 people were injured as a result of the tornado.[37]
November 4
[edit]An IF1.5 tornado struck parts of Dereköy, Turkey.[38]
Europe
[edit]Austria
[edit]On May 6, an F1 tornado struck the town of Ziersdorf and caused damage to outbuildings and the roofs of several homes. A section of roofing from one home was torn off and thrown 50 meters, two cars were damaged by flying debris, and trees and telephone lines were also damaged.[39]
Bulgaria
[edit]On November 4, an intense tornado struck Lavino in Bulgaria. According to the European Severe Storms Laboratory, at least 150 structures were damaged, and one person was slightly injured, earning a rating of IF3. Additionally, an unrated tornado struck parts of Sratsimir, Bulgaria.[38]
Denmark
[edit]A significant tornado impacted the community of Grønhøj Strand in Jammerbugt Municipality on September 19. The tornado picked up a mobile home and threw it 20 metres. Other mobile homes and caravans were overturned or moved and a shed was destroyed. According to the ESSL, the tornado had a track length of 1.2 km, had a maximum path width of 100 metres, and had a maximum intensity of IF2.[40]
France
[edit]March 9
[edit]A strong tornado was caught on video from multiple angles as it impacted areas in and around several small towns and villages in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of France, resulting in extensive damage. The tornado first badly damaged the roof of a school in Masbaraud-Mérignat before it moved to the northeast and struck Pontarion, where multiple homes and other structures had their roofs heavily damaged, and one house was completely unroofed. Vehicles in town were damaged by flying debris, trees and power poles were downed, a large masonry storage building was partially destroyed, and roof tiles and other projectiles were found driven into the exterior insulation layers of homes. The tornado also caused significant tree damage as it moved through wooded areas outside of Pontarion, snapping and uprooting many large trees, while multiple outbuildings were damaged or destroyed as well. Towards the end of the path, 17 homes sustained minor damage in the Le Donzeil area before the tornado dissipated. The tornado was rated F2 by the ESSL (European Severe Storms Laboratory) and the French Observatory of Tornadoes and Violent Thunderstorms (Keraunos).[41] Keraunos noted that the environment where the tornado formed was conducive for tornado development, as high instability and shear were present in France that day.[42][43]
September 17
[edit]Three tornadoes impacted France and the United Kingdom. A brief landspout struck Séreilhac in Région Limousin. [44] Around the same time, a significant tornado struck in Mayenne, France, causing damage to or destroying structures, trees, and concrete utility poles were bent. The French Observatory of Tornadoes and Violent Thunderstorms (Keraunos) rated the tornado EF2 on the Enhanced Fujita scale, with winds estimated between 175 to 225 kilometres per hour (109 to 140 mph).[45] The European Severe Storms Laboratory rated the tornado IF2 on the International Fujita scale.
November 4
[edit]An IF1 tornado struck parts of La Pouëze, France.[38]
Germany
[edit]February 1
[edit]| FU | F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Multiple severe thunderstorms formed in Germany, producing two tornadoes. The first was a short-lived F1 tornado which tracked for 0.2 km (0.1 mi), damaging the roofs of 14 homes in Hinte.[46][47] The second tornado struck areas near the small villages of Getmold, Lashorst and Hedem along a 5.3 km (3.3 mi)-long path, snapping or uprooting large trees and heavily damaging the roofs of multiple homes. A car was damaged by a falling tree near Lashorst, a carriage house had its roof torn off, and a carport was damaged at a farmstead. The most significant damage occurred in an area of pine forest, where many large trees were completely mowed down or stripped of their limbs, and a few tree trunks were snapped off and thrown some distance into nearby fields. Based on the severe tree damage, the second tornado was given an F2 rating.[46][48] Over 85 severe weather reports were documented in Europe that day, 69 of those in Germany.[46][49]
September 21
[edit]Severe thunderstorms spawned at least one tornado in western Germany, which affected the towns of Nusbaum and Mülbach. Severe damage to roofs and trees was reported, and the tornado has been given a preliminary IF2 rating by the ESSL.[50]
Greece
[edit]November 4
[edit]a significant tornado struck Xánthi, Greece. A large tree branch fell on a moving bus, causing no injuries. Length of the damage path reached at least 1.5 km (between Geor. Kondyli street and EPS stadiums). This tornado was rated IF2. [38]
November 25
[edit]A tornado was observed in Phalasarna. Significant damage occurred to greenhouses and trees, earning a rating of IF2.[38]
Ireland
[edit]A significant tornado touched down in Leitrim, County Leitrim, in Ireland on December 10. The tornado, which was filmed from multiple angles, minorly injured two people. The European Severe Storms Laboratory rated the tornado IF2 due to building roof damage.[51][52][53]
Italy
[edit]January 17
[edit]On January 17, a brief but strong tornado struck Valmontone, which is a comune in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, causing significant damage and injuring 2 people. The tornado was spawned by an embedded "comma head" circulation and was captured by a surveillance camera. Multiple homes, apartment buildings, and other structures suffered severe roof damage, and the top floor of one residence was completely destroyed. Trees, gates, and fences were knocked down, and debris was strewn across yards and roads. The European Severe Storms Laboratory rated the tornado F2 on the Fujita scale, with a path length of 2.7 kilometres (1.7 mi) and a maximum width of 150 metres (160 yd).[46] After the tornado, Valmontone declared a state of disaster.[54]
April 10
[edit]On April 10 a small outbreak occurred in the Greater Mediterranean. The most significant tornado touched down in Turkey. A waterspout made landfall near Pizzo in Southern Italy, causing no damage.[36]
July 22
[edit]A strong tornado tracked 14 km in and around Alfonsine, Emilia Romagna, injuring 14 people. Steel power trusses were bent at the base, cars and trucks were moved, heavy damage occurred to crops of various types, trees were snapped or uprooted, objects were lofted for hundreds of meters, and some buildings (partially) collapsed. The tornado was rated IF3 on the International Fujita scale by the European Severe Storms Laboratory.[55]
August 1
[edit]A tornado had occurred near Jesolo as part of the storm system that produced a tornado in Slovenia.[56]
November 2
[edit]An IF1 rated tornado struck parts of Castel Focognano in Italy, damaging roofs and trees.Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).[57] The tornado was rated IF2.5 by the European Severe Storms Laboratory on the new International Fujita scale (IF-scale).[38] On November 6, TORRO released a statement that rated the tornado T6 on the TORRO scale, which is equivalent to a low-end F3 tornado.[58]
Slovenia
[edit]A rare tornado touched down in Ilirska Bistrica, Slovenia, damaging houses and felling trees. The tornado, which was rated F1/T3, was associated with an isolated supercell storm. Tornadoes are exceedingly rare in Slovenia and neighboring countries except for Italy. The nearest official weather station, Koseze, reported 107 km/h (30 m/s; 66 mph) winds some distance from the tornado's path.[59][60] The region had been the site of uncommonly severe storm systems throughout June and July 2023.[citation needed]
United Kingdom
[edit]September 17
[edit]Three tornadoes impacted France and the United Kingdom. In the late evening, a waterspout made landfall on West Beach before tracking through the western and northern suburbs of Littlehampton and then the communities of Wick and Lyminster. This tornado toppled several trees, smashing at least 20 car windows and those of multiple houses. One person sustained minor leg injuries. On September 18, the Met Office noted that "conditions weren't unfavourable" for a small tornado.[61][62] On September 19, a TORRO site investigator confirmed the event as a tornado. A preliminary analysis suggested the majority of the damage warranted a T1 rating, with a peak of T2.[63]
October 28
[edit]For the second time in just over a month, another tornado struck the town of Littlehampton. Several trees were snapped, fence panels were destroyed, power lines were brought down, car windows were smashed, and one house had its entire roof ripped off. On October 29, a TORRO site investigator visited the site where the event happened and confirmed that the weather event was a tornado. Additionally, they have provisionally rated the tornado T4 on the TORRO scale, which is equivalent to a low-end F2 tornado.[64] The European severe weather database rated the tornado IF2 on the International Fujita scale. [65]
November 2
[edit]On the morning of November 2, a tornado was confirmed in Sompting and northern Lancing in West Sussex. According to TORRO after looking at the damage caused and reports from the public, the tornado’s track was mapped, and the tornado was rated a T2 on the TORRO scale.[38]
North America and Caribbean
[edit]Canada
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 56 | 21 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 82 |
- Note: One tornado has been confirmed but is unrated.
July 1
[edit]A violent EF4 tornado, estimated at 620 m (680 yd) wide, struck Mountain View County, Alberta, Canada, at 1:45 p.m. MDT (19:45 UTC). Areas between Didsbury and Carstairs were hit hardest before the tornado crossed Highway 2. Three homes were destroyed, four were rendered uninhabitable, and five were damaged.[66] One person was injured by debris while sheltering in the basement of her collapsing home, but no fatalities occurred. Tree branches were snapped, power lines were downed, and one gas leak occurred at a destroyed home. Twenty-five cows, twenty chickens, and one horse were also killed.[67] Significant ground scouring occurred near Didsbury.[68] The joint damage survey from Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC), Prairie and Arctic Storm Prediction Centre (PASPC), and the Northern Tornadoes Project (NTP) assigned a maximum rating of low-end EF4 based on one well-built home being completely destroyed, with peak wind speeds estimated at 275 km/h (171 mph). Near this home, a 22,000 lb (10,000 kg) combine was thrown 50 m (160 ft) before being rolled a further 50 to 100 m (160 to 330 ft). This was only the third violent tornado in Alberta history, after the 1987 Edmonton tornado and the 1915 Grassy Lake tornado (also known as the Redcliff Cyclone).[66]
July 13
[edit]The next day, the storms moved into Southern Ontario and Quebec, where three tornadoes were confirmed by Environment and Climate Change Canada. The first two both touched down in the Ottawa suburb of Barrhaven one minute apart; 125 homes were damaged between the two and one person suffered minor injuries.[69] The third, unrated tornado touched down near Montréal–Mirabel International Airport, although no injuries or damage were reported. The storm also caused 500,000 people to lose power across Southern Quebec.[70]
August 24
[edit]In Ontario, two tornadoes occurred simultaneously and moved southeastward in the Windsor area.[71] The first one was an EF0 tornado that moved through the west side of Windsor, downing numerous trees and branches, removing roof shingles from homes, and damaging fences.[72] To the east, an EF1 tornado collapsed barns, snapped power poles, damaged grain bins, downed trees and branches down, and removed roof shingles from numerous homes as it passed east of Tecumseh and struck Elmstead before dissipating northeast of Pleasant Park.[73]
Severe flooding and damaging winds also affected much of the region and three deaths occurred after a weather-related vehicle accident.[74] This outbreak also produced tornadoes in adjacent U.S. states and between the two nations, estimated economic losses reached $880 million.[75] Tornadoes were also recorded in Newfoundland and Labrador.[citation needed]
Puerto Rico
[edit]A high-end EF1 tornado touched down in Aguada, Puerto Rico on July 16, partially tearing the roof off of one home causing significant interior damage. Another home lost its roof covering material and metal siding. Numerous trees were uprooted and snapped. Peak wind speeds were estimated at 110 mph (180 km/h).[76]
United States
[edit]Approximate touchdown location of killer tornadoes in 2023 Summary of tornadoes[77]
|
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 431 | 430 | 125 | 29 | 2 | 0 | 1,268 |
- Note: One tornado has been officially confirmed but is not yet rated.
January 2–4
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 25 | 24 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

In early January, a three-day severe weather outbreak brought damaging winds, large hail, and numerous tornadoes to the Southern United States and impacted the Midwestern United States to a lesser extent. On January 2, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for all of Arkansas and parts of surrounding states, with a 10% hatched risk for tornadoes. An EF1 tornado damaged homes and the high school in Jessieville, Arkansas, injuring two people.[78][79][80] A large 1.1-mile-wide (1.8 km) EF2 tornado caused severe damage near Jonesboro, Louisiana, snapping many large trees, inflicting significant damage to several residences, and injuring three people.[78] Another strong EF2 tornado knocked down metal truss electrical transmission towers near Haile and destroyed an outbuilding. A third large, long-tracked EF2 tornado damaged or destroyed multiple houses, vehicles, and a mobile home in Montrose, Arkansas, and snapped or uprooted countless trees and many power poles along its path.[78][81] The next day, another enhanced risk was issued farther east in the Gulf Coast region, with a 10% hatched risk area for tornadoes in place for parts of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. An EF2 tornado downed many large trees, tore most of the roof off a house, caused roof damage to other homes, and destroyed boathouses and outbuildings at the Jordan Lake Reservoir near Deatsville, Alabama. Several tornadoes touched down as far north as Illinois, including two separate EF0 and EF1 tornadoes that caused damage to outbuildings and farm equipment near Maroa. Another pair of EF1 and EF0 tornadoes also briefly touched down in Decatur, with the EF1 tornado damaging a vacant bowling alley and the EF0 tornado causing minor damage at Richland Community College. Tornadoes continued touching down into the morning of January 4, including a high-end EF1 tornado that damaged several homes, flipped cars, and severely injured a person on the eastern side of Montgomery, Alabama. In Georgia, an EF1 tornado struck the small community of Roosterville, where a barn and a mobile home were destroyed. An EF1 tornado also struck Sandersville, where homes and a warehouse were damaged and many trees were downed, some of which landed on structures. A semi-truck was overturned in Sandersville, injuring the driver.[78][82] Additional weak tornadoes touched down across parts of the Carolinas later that day before the outbreak came to an end.
Widespread flooding also occurred as a result of the storm system, with 8.55 in (217 mm) of rain in DeWitt, Arkansas, and 4.99 in (127 mm) of rain in Greenville, Kentucky. Cane Creek State Park recorded 7.30 in (185 mm) of rain, their largest 24-hour total on record.[83] Daily rainfall records were also established in Memphis, Tennessee, and Jackson, Mississippi, with Amtrak's northbound City of New Orleans being delayed due to flooding and debris on the tracks between the two cities.[84][85][86][87] Further north, Minneapolis-St. Paul International Airport instituted a ground stop due to the snow and ice,[88] in what became the 4th largest January snowstorm for the region.[89] One fatality occurred due to the snowstorm as a result of a car crash in Clearwater Township, Minnesota.[90] Overall, a total of 58 tornadoes were confirmed.
January 12
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8 | 20 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 0 |

A significant tornado outbreak impacted the Southeastern United States, with several strong and long-tracked tornadoes touching down and causing multiple fatalities. On January 12, the SPC issued an enhanced risk of severe weather, including a 10% risk area for tornadoes. Multiple supercell thunderstorms formed in the threat area later that day, and significant tornadoes began touching down. In Alabama, the small towns of Emelle, Eutaw, and Movico were all impacted by EF2 tornadoes, resulting in extensive damage. A large high-end EF2 tornado also caused severe structural damage in Selma, Alabama. Many homes and businesses sustained major damage in Selma, and a daycare with 70 children plus workers was destroyed, but only one minor injury occurred inside, one of two injuries reported from the tornado. The same storm that produced the Selma tornado later produced a long-tracked EF3 tornado that prompted tornado emergencies for Autauga, Elmore, Chilton, Coosa, and northern Tallapoosa counties.[91] This deadly tornado caused seven fatalities in the Old Kingston community of Autauga County as it completely obliterated numerous mobile homes, as well as tossing vehicles and causing massive timber damage.[92] Multiple strong tornadoes, which were all spawned by the Selma supercell, also impacted parts of Georgia, including an EF2 tornado that inflicted major damage to homes and industrial buildings in the southern part of LaGrange. A large EF3 tornado struck the western edge of Griffin and Experiment, badly damaging or destroying homes and businesses, and flipping cars. This tornado was accompanied by three other tornadoes at the beginning of its track near Griffin, including a high-end EF2 tornado that caused considerable damage to homes and trees. Another high-end EF2 tornado also caused significant damage in Jenkinsburg and near Jackson Lake, resulting in one fatality when a tree fell onto a car along with an indirect fatality the next day when falling tree limb knocked a transportation worker out of a bucket truck while he working to restore power lines.[93] A high-end EF1 tornado also touched down near the Atlanta suburb of Mableton, damaging an industrial business and downing many trees, some of which landed on homes. Other weak tornadoes were confirmed in parts of Mississippi, Tennessee, Kentucky, Illinois, and the Carolinas. Overall, this outbreak produced a total of 41 tornadoes and resulted in eight fatalities, along with at least 53 injuries.[94]
January 22
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A line of severe storms produced damaging straight-line winds and multiple tornadoes in the Florida Panhandle and Southeast Georgia throughout January 22, including two low-end EF2 tornadoes. The first one struck the community of Turquoise Beach, Florida, to the northeast of Santa Rosa Beach, downing trees and damaging several homes. Three of the damaged houses had significant portions of their roofs uplifted.[95] The other strong tornado struck the northern side of Adel, Georgia, shifting multiple buildings off their foundations, including a metal structure that was completely destroyed. It also destroyed a motorhome, knocked over a series of centerline irrigation pivots, and damaged trees, some of which fell on homes.[95] Three EF1 tornadoes also touched down elsewhere in Georgia that day, bringing the final tornado tally to five.[78]
January 24–25
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |

On January 24, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for much of the Gulf Coast region, including a 10% hatched risk area for tornadoes. Throughout the day, a small but significant outbreak of tornadoes impacted the Southern United States, primarily from Southeast Texas to southern Louisiana. Multiple strong tornadoes were confirmed, including a large and destructive low-end EF3 tornado that moved through the southeastern sections of the Houston metropolitan area, impacting the suburbs of Pasadena and Deer Park.[96] This prompted the issuance of a tornado emergency, the first ever issued by the National Weather Service's forecast office in Houston.[97][98] The intense rain-wrapped tornado inflicted major structural damage to many homes, apartment buildings, churches, and businesses, and downed many trees and power lines. Cars were thrown and mangled, a metal building was destroyed, a senior center sustained major damage, and metal truss electrical transmission towers were toppled to the ground. No fatalities occurred as a result of the EF3 Houston metro tornado, though a few minor injuries were reported. The tornado caused $6.6 million in damage.[99][100] The same storm also produced two EF0 tornadoes that caused minor damage in the Houston suburbs of Sienna and Pearland prior to spawning the EF3 tornado. Elsewhere, a brief EF2 tornado unroofed a house and destroyed a barn near Nome. Three people were injured by another EF2 tornado that touched down near Orangefield before striking the outskirts of Orange, causing major damage to mobile homes, houses, and outbuildings before crossing into Louisiana and inflicting more severe damage to numerous structures north of Vinton. Several metal buildings were also damaged, and many large trees were snapped or uprooted by this tornado as well. In Louisiana, another EF2 tornado struck the small community of Gaytine, where houses had their roofs torn off, a mobile home was destroyed, a metal building was heavily damaged, and a fifth-wheel RV trailer was flipped. In Ventress, three people were injured by an EF1 tornado that destroyed a few mobile homes.[101] Three additional weak tornadoes touched down in Florida on January 25 before the outbreak came to an end. A total of 15 tornadoes were confirmed. In addition to the tornadoes, the storms also produced flash flooding and a daily record for rainfall was set in Houston, at 4.05 in (103 mm).[102] The flash flooding forced SH 99 to temporarily close.[103]
February 8–9
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

On February 8, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk of severe weather for parts of Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana, including a 10% hatched risk area for tornadoes. A line of severe storms produced damaging straight-line winds and multiple tornadoes in Mississippi and Louisiana throughout the day, a couple of which were strong. An EF2 tornado struck the village of Tangipahoa in eastern Louisiana, damaging trees and structures in town, including a church and gas station convenience store. Numerous mobile homes were damaged or destroyed in town, a vacant business was unroofed, and many trees were snapped or uprooted as well. Another EF2 tornado struck the community of Grand Prairie, Louisiana, where a well-built home had its roof torn off and trees were snapped. A few other homes and outbuildings along its path suffered more minor damage. Several other weaker tornadoes touched down during the evening across the same region. After roughly 24 hours of no activity, a ninth tornado associated with the same storm system touched down in the Florida Panhandle late on February 9, snapping or uprooting numerous trees near Eucheeanna. In total, nine tornadoes were confirmed.[78]
February 16–17
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

On February 16, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for parts of the Southeastern United States and the Ohio Valley region, including a 10% hatched risk area for tornadoes in parts of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee. Severe thunderstorms developed later that day, producing damaging winds, large hail, and several tornadoes, a couple of which were strong. An EF2 tornado near Pindall, Arkansas, destroyed barns, pushed a house off its foundation, snapped trees, and injured two people.[104] Another EF2 tornado injured one person, snapped many trees, and knocked over a few metal truss electrical transmission towers near Ripley, Mississippi, before weakening and striking the north edge of town, where a few homes and businesses sustained minor damage. An EF1 tornado that occurred near Wesson, Mississippi, rolled and destroyed a mobile home, and damaged two other residences. An EF1 tornado near Ramer, Tennessee, inflicted heavy roof damage to a home and destroyed two garages, and another EF1 tornado near Lewisburg damaged homes, destroyed barns and outbuildings, and downed trees. On February 17, an EF1 tornado caused considerable damage as it moved through the south side of LaGrange, Georgia, not far from where a damaging EF2 tornado had struck the prior month. Many trees were snapped or uprooted in LaGrange, while homes and businesses sustained roof and window damage. Overall, a total of 13 tornadoes were confirmed. In addition to tornadoes, straight-line winds from the system led to a tree falling at the Northwestern University campus, injuring four people.[105] Flooding caused by the storms also killed two people, one in Kentucky and one in West Virginia.[106] Flooding also resulted in I-65 being shut down near Cullman, Alabama.[107]
February 21
[edit]An EF2 tornado touched down in Mercer County, New Jersey, only the fifth February tornado to touch down in the state during February, and the first F2/EF2 to touch down in the state since February 2, 1973.[108][109] The storm resulted in Quakerbridge Road being blocked off in Lawrence Township and Hamilton Township.[110] U.S. Route 1 was also closed in both directions in Lawrenceville as a result of the storm.[111] Around 75 residents were displaced due to the tornado, with 27 residences being rendered uninhabitable.[112]
February 26–27
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 14 | 11 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

On February 26, a large storm system produced a wide range of significant weather events across a large area of the United States, ranging from heavy snow to tornadoes. The Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk for west-central Oklahoma for a 45% hatched risk area for damaging winds. The outlook also included a 10% hatched risk area for tornadoes. An enhanced risk also extended from the Texas Panhandle to southwestern Missouri. Aided by very strong wind shear, a powerful squall line of severe thunderstorms containing damaging straight-line winds and multiple embedded QLCS tornadoes formed and moved through the risk area later that night. A high-end EF2 tornado obliterated manufactured homes, tossed vehicles, and killed one person as it moved through the outskirts of Cheyenne, Oklahoma, injuring three others as well.[113] The line of severe storms also produced five tornadoes that impacted areas in and around the Oklahoma City metropolitan area, a couple of which were strong. This included a high-end EF2 tornado that struck the southeastern part of Norman, where homes and businesses sustained major damage, self-storage units were destroyed, cars were flipped, and 12 people were injured. Another high-end EF2 tornado also caused significant damage to homes and other structures near Shawnee. In addition, there were widespread reports of damaging straight-line winds that reached up to 70–80 mph (110–130 km/h), with locally higher gusts reported, including a 114 mph (183 km/h) wind gust in Memphis, Texas.[114][115] Tornadic activity continued the next day in Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio as the system pushed eastward. Several weak tornadoes occurred, including a high-end EF1 tornado that touched down in Jacksonburg, Ohio, before it passed near Middletown, causing considerable damage to a few homes, barns, and trees. In all, 30 tornadoes were confirmed, resulting in one tornado-related fatality; the 12 tornadoes in Oklahoma set the record for the most tornadoes ever recorded in the state in the month of February. In addition, there were 12 other non-tornado-related fatalities that occurred as a result of the storm system.[116]
March 1–3
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 9 | 22 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

In early March, a powerful storm system brought widespread severe weather, including multiple tornadoes, across a large portion of the Eastern United States. On March 1, the Storm Prediction Center outlined an enhanced risk across areas in Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Tennessee, including a 10% hatched risk for tornadoes.[117] In Shottsville, Alabama, a low-end EF1 tornado caused minor damage to a church, before downing trees and damaging the roof of a house elsewhere along the path. A stronger, but short-lived high-end EF1 tornado touched down in a subdivision near Hazel Green, Alabama, where a few homes sustained extensive damage and a vehicle was flipped onto its side. On March 2, the Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk for the following day for parts of Texas, Arkansas, and Louisiana. A 15% hatched risk for tornadoes was in place across the Ark-La-Tex region, with the potential for strong tornadoes noted, although this was downgraded to a 10% hatched area due to lingering uncertainties about the convective modes that day. However, a 45% hatched area for wind damage was also in place in the same general area as well. A high-end EF2 tornado completely demolished two chicken houses and a mobile home, snapped many trees and power poles, partially unroofed a house, and injured five people near Kirby, Arkansas.[118] Several other tornadoes touched down throughout the threat area, though all were weak. This included an EF1 tornado that damaged numerous homes and a few businesses as it moved through the southeastern side of Shreveport, Louisiana, injuring two people. A high-end EF1 tornado also damaged multiple buildings as it impacted Pickton, Texas. On March 3, the storm system moved into the Ohio Valley region, where an EF2 tornado in the small community or Fremont, Kentucky, destroyed outbuildings, heavily damaged a church, and tore the roofs off of a few homes. In Vanderburgh County, Indiana, an EF1 tornado unroofed a church and damaged many homes and trees in the Saint Joseph community. Another EF1 tornado tracked from Duff to the northwestern part of Jasper, downing many trees, damaging or destroying a few barns, and inflicting roof and siding damage to homes. In Highland County, Ohio, an EF1 tornado caused considerable damage to homes and outbuildings in and around Pricetown, downed numerous trees and tree limbs, and tore much of the roof off a church elsewhere along its path. Farther south, two EF1 tornadoes in Alabama caused minor to moderate damage in and around Section and Rosalie. An EF1 tornado also downed many trees in and around Gray Court, South Carolina, some of which landed on houses. In addition to the tornadoes, the severe thunderstorms brought numerous reports of damaging straight-line winds and flooding. Overall, a total of 33 tornadoes were confirmed. While no tornado-related fatalities occurred, at least 13 non-tornado-related deaths occurred as a result of the storm system.[119][120]
March 22
[edit]On the morning of March 22, a high-end EF1 tornado impacted the Los Angeles suburb of Montebello, causing considerable damage. The tornado moved through an industrial area, where multiple warehouses had large sections of their roofs torn off. One warehouse sustained almost total collapse of its roof and had an HVAC unit ripped off. Signs were damaged or destroyed, windows were shattered, and numerous vehicles were damaged by flying debris. A power pole and some trees were downed, a semi-trailer was tipped over, and debris was scattered throughout the area. One person was injured. This was the strongest tornado to impact the Greater Los Angeles metro area since 1983.[121][122][123] The storm also brought 1.01 in (26 mm) of rain to Los Angeles, breaking a daily rainfall record.[124]
March 24–27
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 18 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 |

Beginning on March 24, a four-day severe weather and tornado outbreak impacted the Southeastern United States. The outbreak began in the morning with two EF1 tornadoes causing injuries in Texas before more significant tornadoes impacted Mississippi that night. One long-tracked and violent high-end EF4 tornado with wind speeds up to 195 mph (314 km/h) prompted a tornado emergency for Rolling Fork and Silver City, causing major damage in both communities, with widespread and catastrophic damage occurring throughout much of Rolling Fork. A total of 17 people were killed by the Rolling Fork tornado. Another intense tornado from the same storm prompted another tornado emergency as it struck Winona; three people were killed by this EF3 tornado. Another destructive EF3 tornado from the same storm also caused major damage near or in the communities of Egypt, New Wren, and Amory, resulting in major damage and two fatalities. More tornadoes touched down in Alabama and Tennessee later that night and into the early morning hours of March 25, including an EF2 tornado that caused damage in Fayetteville, Tennessee, and another EF2 tornado that killed one person in Hartselle, Alabama, early on March 25.[125][126][127] From March 26 into March 27, the slow-moving storm system completely stalled out, and more severe weather occurred over the next two days as well, producing several additional tornadoes, including an EF3 tornado that struck just north of West Point, Georgia, on March 26, causing major damage to trees and houses and injuring five people. A total of 33 tornadoes were confirmed as a result of this outbreak, which killed 23 people and injured many others.
March 31 – April 1
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 45 | 47 | 32 | 11 | 1 | 0 |

A large, widespread, and deadly tornado outbreak impacted large portions of the Midwestern, Southern, and Eastern United States. A high risk was issued for two areas in the Mississippi Valley on the morning of March 31; it was the first high risk issuance since March 25, 2021. That afternoon, a high-end EF3 wedge tornado passed through the Little Rock, Arkansas, metro area, prompting a tornado emergency as it inflicted significant damage to numerous structures. One person was killed by that tornado. Later, an intense high-end EF3 tornado caused severe damage near Martinsburg, Iowa. The same storm then produced a violent low-end EF4 tornado that destroyed multiple homes near Keota. The Iowa towns of Coralville, Hills, Mediapolis, and Charlotte all sustained significant damage after being impacted by EF2 tornadoes. EF2 tornadoes also caused severe damage in Sherman and Geneseo, Illinois, as well. Several other large tornadoes touched down throughout that afternoon and evening, including an EF3 tornado that killed four people in Wynne, Arkansas, and another EF3 tornado that killed a person in Covington, Tennessee. An EF1 tornado that struck Belvidere, Illinois, collapsed the roof of the Apollo Theatre, which was hosting a sold-out concert, resulting in one fatality and over 40 injuries.[128] Later, another destructive EF3 tornado killed six people when it struck Robinson, Illinois, and Sullivan, Indiana, before the cell traveled northwest, producing another EF3 tornado that destroyed homes, tossed cars and farm machinery, and killed two people near Spencer. The same supercell later spawned an EF3 tornado which directly impacted the town of Whiteland, where a warehouse and many homes were destroyed.[129] Another destructive and long-tracked EF3 tornado killed nine people in McNairy County, Tennessee, impacting the outskirts of Bethel Springs and Adamsville. A high-end EF3 tornado north of Hazel Green, Alabama, also destroyed homes and killed a person early on April 1.[78][130][131][132] More severe weather occurred the next day along the eastern Great Lakes and East Coast, producing widespread damaging winds along with isolated hail and tornadoes. This included one destructive EF3 tornado that killed a person in Sussex County, Delaware. The tornado was the largest ever recorded in Delaware and only the second killer tornado and the second tornado rated F3/EF3 in the state since modern records began in 1950.[78][133][134][135] Seven tornadoes also touched down in New Jersey, three of which reached EF2 intensity.[78][133] In all, 147 tornadoes making it the 3rd largest tornado outbreak in recorded history, along with 26 tornadic fatalities, one indirect tornado-related fatality, and at least 218 injuries were confirmed as a result of this tornado outbreak. Six non-tornadic deaths also occurred during the outbreak.[136]
April 4–5
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 10 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |

Another severe weather and tornado outbreak affected the Midwestern United States, Mississippi Valley, and Great Lakes in early April. On April 4, a moderate risk was issued by the SPC for parts of Illinois and Iowa, with a second moderate risk outlined for parts of Arkansas and Missouri. A 15% hatched risk area for tornadoes was in place for both moderate risk areas. Multiple tornadoes touched down throughout the afternoon and evening, including two EF1 tornadoes that touched down in the Quad Cities metro area, downing trees and damaging the roofs of homes in Rock Island and Moline, Illinois. Near Pleasantville, Iowa, a narrow and highly photogenic high-end EF1 tornado was caught on video by many storm chasers, and caused damage to homes and outbuildings. The most intense tornado of the event was a large high-end EF3 tornado that destroyed homes and injured four people near Lewistown, Illinois, before striking Bryant, causing significant damage in the small village. A storm chaser's vehicle was rolled by the tornado, though he was not injured.[137] A brief EF2 tornado ripped the roof off a gas station in Colona, while another EF2 tornado destroyed outbuildings and uplifted the roof of a house near Geneseo. A high-end EF1 tornado also caused damage to homes, garages, and trees in Table Grove. During the early morning hours of April 5, a nighttime high-end EF2 tornado struck the communities of Grassy and Glen Allen, Missouri, causing severe damage as multiple homes had their roofs torn off, a few of which sustained failure of exterior walls. Outbuildings and mobile homes were also obliterated by the tornado, with five people being killed in one of the mobile homes.[138][139][140] This became the deadliest tornado in Missouri since the 2011 Joplin tornado.[141]
Weak tornadoes continued to touch down across parts of the Ohio Valley later that day, including three EF1 tornadoes that caused considerable damage in the Louisville, Kentucky, metro area. One of these tornadoes reached high-end EF1 strength and unroofed an apartment building in the Pleasure Ridge Park neighborhood. The other two tornadoes damaged warehouses and businesses in the suburb of Watterson Park, one of which damaged the Yum! Brands headquarters. A non-tornadic fatality occurred in Louisville when a man who was walking his dog was killed by a falling tree.[142] Farther east, an EF0 tornado caused minor damage in the town of Pleasantville, Ohio. As a result of the storms, the Cincinnati Reds game against the Chicago Cubs was postponed,[143] while Chicago O’Hare International Airport had a ground stop.[144] The anticipated severe weather in the Eastern United States on April 6 resulted in the New York Mets, Baltimore Orioles, and Philadelphia Phillies postponing their home openers.[145][146][147] In all, five tornado-related fatalities and 27 tornadoes were confirmed, with one non-tornadic fatality as well. The National Centers for Environmental Information documented that this storm system caused $2.2 billion (2023 USD) in damage.[148]
April 15
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

On April 15, a linear complex of severe thunderstorms with embedded circulations developed in Missouri and moved eastward through the St. Louis metro area, producing multiple tornadoes. A strong EF2 tornado destroyed a small house near Vichy, Missouri, heavily damaged metal airplane hangars at Rolla National Airport, and injured five people. An EF1 tornado moved through the St. Louis suburbs of Fenton and Sunset Hills, causing damage to homes, warehouses, and trees. The towns of Hillsboro, Festus, and Pevely were also directly hit by EF1 tornadoes, resulting in minor to moderate damage. Another EF1 tornado struck Belleville, Illinois, where homes, apartment buildings, and businesses had roofing blown off and large trees were snapped or uprooted, some of which landed on structures. Farther south, an isolated EF1 tornado caused damage to trees and homes near Ringgold, Louisiana. A total of 14 tornadoes were confirmed, and numerous reports of damaging straight-line winds were received as well.[78][149] The National Centers for Environmental Information documented that this storm system caused $1.1 billion (2023 USD) in damage.[148] The line of storms also forced the Kansas City Royals to postpone a baseball game against the Atlanta Braves.[150]
April 19–20
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
On April 19, a tornado outbreak impacted areas in the southern Great Plains. In Oklahoma, 18 tornadoes touched down and moved erratically near the southern and eastern outskirts of the Oklahoma City metropolitan area. Several of the tornadoes were strong, and most of them were produced by a large, slow-moving supercell that moved east-northeastward.[151][152] A large high-end EF3 tornado impacted the community of Cole, heavily damaging or destroying homes, mobile homes, and other structures, resulting in a fatality. An indirect fatality from the tornado was also confirmed.[153][154][155][156][157][158] The supercell also produced multiple weak tornadoes and two large, high-end EF2 tornadoes that caused significant damage near Etowah,[159] before merging with another tornadic supercell to its west. This cluster of storms spawned a large, broad mesocyclone that produced several circulations that rotated around each other due to the Fujiwhara effect.[159][160] These circulations produced multiple erratic-moving strong tornadoes after sunset, including EF3 and EF2 tornadoes south and north of Pink respectively, and a very large, high-end EF2 tornado that struck Shawnee, where numerous homes and other buildings sustained extensive damage or were destroyed, including buildings at Oklahoma Baptist University and Shawnee High School. A news-gathering Bell 206 B3 JetRanger helicopter operated by Tulsa television station KOTV was damaged at the Shawnee Regional Airport, along with several hangars.[161][162][163][164]
Further north, a supercell produced a series of eight tornadoes in Chase County, Kansas, near Strong City, including an EF0 tornado that overturned a semi-truck near Elmdale, causing an injury. Two EF2 tornadoes near Strong City caused major damage to outbuildings, silos, power poles, and trees, while an EF0 tornado caused minor tree damage in the northern part of town. An EF1 tornado caused minor to moderate damage as it moved through Cottonwood Falls, and another EF0 tornado injured a person in a vehicle near Saffordville. Three EFU tornadoes were also confirmed in Iowa.[165] Another round of severe weather occurred the next day from southern Wisconsin to South Texas, including three weak tornadoes in Illinois and Texas, and hail in Illinois up to 3.00 in (7.6 cm) wide.[166][167] Federal disaster assistance was requested in Oklahoma following the tornado outbreak. Overall, a total of 32 tornadoes were confirmed. One direct tornado-related fatality occurred, along with an indirect fatality and 188 injuries.[168][169] The tornado outbreak resulted in $1.9 billion in damage.[148]
April 22
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

Several tornadoes touched down in the Eastern United States on April 22. An EF0 tornado in Mooresville, North Carolina, caused minor tree, fence, and house damage. Another EF0 tornado touched down in Poolesville, Maryland, where minor tree and structure damage occurred. The town of Womelsdorf, Pennsylvania, was struck by an EF1 tornado, which snapped trees and power poles, damaged a few structures and vehicles, and flipped a set of metal bleachers. The most significant tornado of the event was an EF2 tornado that produced its most intense damage in rural forested areas north of Jeffersonville, New York, where a metal truss transmission tower was collapsed, garages and barns were heavily damaged or destroyed, and many large hardwood trees were snapped or uprooted. The tornado unroofed a couple of buildings in Roscoe and Rockland shortly before it dissipated. Two children were killed in Pennsylvania as a result of trees that were blown over by straight-line winds. The next morning, heavy rainfall fell in the Northeast, with a daily record of 3.13 in (80 mm) of rain in Hartford, Connecticut.[170] The rainfall total in Central Park was 2.14 in (54 mm).[171] A total of eight tornadoes were confirmed.[78][172]
April 27–30
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |

In late April, a slow-moving weather system produced scattered tornadoes in the Southern and Eastern United States throughout a four-day period. On April 27, the Storm Prediction Center issued a slight risk of severe weather for the Gulf Coast region, including a 5% risk of tornadoes. A strong EF2 tornado struck the small town of Hosford, Florida, downing many trees and inflicting major damage to a few homes. A high-end EF1 tornado caused damage in Lynn Haven, while a few other weak tornadoes touched down in other parts of Florida and Georgia. On April 28, an EF0 tornado caused minor damage in Boynton Beach, a brief EF0 tornado also caused minor damage near Elkin, North Carolina, and an EF1 tornado downed many trees and injured two people at Fort Hood (now Fort Cavazos) in Texas. On April 29, the Storm Prediction Center issued a slight risk of severe weather for most of Florida and southeast Georgia, including a 5% risk area for tornadoes. A MCS off the coast of Florida produced damaging straight-line winds and heavy rain throughout the day. In Palm Beach Gardens, Florida, a high-end EF2 tornado a partially unroofed an apartment building, largely destroyed a manufactured home, heavily damaged a dry-cleaning business, and downed many trees and large metal light poles. Along US 1, the tornado was caught on video as it flipped and tossed cars. During the early morning hours of April 30, a high-end EF1 tornado destroyed a metal storage building in rural Charlotte County, Florida. Later in the afternoon, clusters of severe storms affected South Carolina, eastern North Carolina and the Hampton Roads area in Virginia. One embedded supercell made its way into the northern sections of Virginia Beach, Virginia, and produced an intense EF3 tornado that touched down in residential areas of the city, snapping or uprooting trees, overturning vehicles, and causing significant structural damage. Multiple large and well-built homes had their roofs torn off and suffered collapse of their top floor exterior walls. The tornado then struck Fort Story, where buildings sustained less intense damage before the tornado moved out into the Atlantic Ocean. Numerous videos and photographs taken by Virginia Beach residents showed a "stovepipe" tornado with an audible roar. In addition to tornadoes, flash flooding affected the entire East Coast on April 30.[173] A total of 12 tornadoes were confirmed.[78]
May 6–7
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Early on May 6, a line of severe storms pushed through southern Louisiana, producing damaging winds. One low-end EF1 tornado near Morse damaged several homes, destroyed outbuildings, and injured one person.[174] Later that day, a severe weather outbreak impacted the Central United States. Multiple tornadoes touched down in Minnesota and South Dakota, but all were weak and remained over open country, causing no damage. In Missouri, a lone supercell thunderstorm produced multiple tornadoes, including one high-end EF0 tornado that damaged the roofs of several homes and a church in Trenton, as well as a high-end EF2 tornado north of Linneus that damaged or destroyed several homes and outbuildings. The next morning, an EF1 tornado struck the Indiana University Southeast campus in New Albany, Indiana, downing trees, damaging apartment buildings, and injuring two people. An EF0 tornado also caused minor damage to homes and tree branches in Georgetown.[78][175] An EF1 tornado moved through the western part of Louisville, Kentucky and the suburb of Shively, snapping many trees and downing large tree limbs. In Shelbyville, a brief EF0 tornado caused damage to a gas station and a Stanley Black & Decker plant. Farther west in Iowa, an EF1 tornado damaged large outbuildings, trees, and a batting cage in West Liberty. A Taylor Swift Eras Tour concert in Nashville was delayed multiple hours due to severe storms in the area.[176] A total of 24 tornadoes were confirmed, and damage from the severe weather outbreak totaled $1.1 billion.[148]
May 10–13
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39 | 27 | 23 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

Between May 10 and May 13, a tornado outbreak affected the Great Plains. On May 10, multiple weak tornadoes touched down in Colorado, including an EF1 tornado that unroofed a cabin near Woodrow. A couple of EFU tornadoes that caused no damage were confirmed in Arkansas and Kansas as well. On May 11, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for the central Great Plains and a slight risk for part of the Gulf Coast. Numerous tornadoes touched down in both areas, though all were weak.[177] This included an EF1 tornado that downed trees and damaged buildings in Shreveport, Louisiana, and a high-end EF1 multiple-vortex tornado that caused considerable damage to school buildings, outbuildings, homes, and power poles in Weskan, Kansas. In Oklahoma, another high-end EF1 tornado heavily damaged homes and destroyed outbuildings near Cole before it weakened and caused minor tree and roof shingle damage at the south edge of Goldsby. An EF1 tornado also struck Noble, where a donut shop had its roof blown off and some other businesses had severe roof damage.[78] The storms also resulted in Denver recording their 8th wettest day on record, and hail forced a ground stop at Denver International Airport.[178] Amtrak's northbound Heartland Flyer was delayed for almost three hours that day due severe warnings north of its station stop in Purcell, Oklahoma.[179][180]
On May 13, another enhanced risk was issued for Nebraska, where a majority of the strongest tornadoes of the outbreak occurred. This included two large EF2 tornadoes that passed near Uehling and Lyons, destroying numerous barns, garages, grain bins, and farm buildings, and damaging several homes. The two tornadoes also snapped many power poles, downed numerous trees, and damaged farming equipment. The Lyons tornado also caused two injuries. A low-end EF2 tornado near North Bend damaged or destroyed grain bins and outbuildings, flipped irrigation pivot sprinklers, and shifted a house slightly off its foundation. A narrow EF2 tornado caused severe tree damage near Chambers, including some debarking.[78][181][182] A high-end EF1 tornado hit the southeastern part of Anselmo, where a shed was flipped, many trees were snapped, and tree branches were driven into building's exteriors. A large multiple-vortex wedge tornado that passed near Greeley and Spalding flipped and bent irrigation pivots, blew out the windows of two vehicles, scoured gravel off a dirt road, and caused damage to trees and power poles. It was rated high-end EF1, though storm chaser and meteorologist Reed Timmer recorded a 163 mph (262 km/h) wind gust as it passed over his Dominator tornado intercept vehicle, indicating that it was capable of producing high-end EF3 damage.[183] Other tornadoes touched down in Oklahoma and Kansas, including a low-end EF2 tornado near Hamlin, Kansas that snapped trees, destroyed an outbuilding, heavily damaged a trailer, and caused less severe damage to a house.[78] Early the next morning on May 13, a high-end EF1 tornado struck Laguna Heights, Texas, where numerous poorly built mobile homes were heavily damaged or destroyed, and a man was killed inside one of them. Businesses and some industrial buildings in Laguna Heights also sustained major damage, and 11 people were injured.[184][185] More tornadoes touched down later that afternoon across Iowa, with a few others occurring in Illinois, Oklahoma, and New Mexico, all of which were weak and caused little to no damage.[186][187] Flooding also inundated basements and roads in Laurens and Knoxville as rainfall totaled near 7 in (180 mm) in some areas in Iowa.[188][189] The threat of tornadoes across Iowa prompted Donald Trump to cancel outdoor rallies in the state.[190] In all, 94 tornadoes were confirmed and damages from the tornado outbreak totaled $2.4 billion.[148]
June 14–19
[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 33 | 35 | 12 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Multiple rounds of severe and tornadic thunderstorms impacted a large portion of the South, Midwest, and Great Plains in the middle of June. On June 14, multiple severe thunderstorm watches and tornado watches were issued from the Ark-La-Tex region to northern Florida, an area that normally does not see this type of extreme weather during that time of year.[191] A large EF2 tornado moved between Blakely and Arlington, Georgia, knocking down power lines and trees and severely damaging a home, injuring the residents inside.[192] More tornadoes were reported later that afternoon and evening across Alabama and Georgia while an EF2 tornado caused major damage in Cass County, Texas.[193] There were also over 300 reports of large hail and damaging winds, including wind gusts reaching as high as 82 mph (132 km/h) and hail up to 5 inches (13 cm) in diameter in Mississippi.[194] On June 15, the Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk for severe weather across much of Oklahoma, along with a small part of Texas and Kansas. The risk was driven by 45% hatched areas for both large hail and damaging winds. A small 10% area for tornadoes covering the eastern part of the Texas and Oklahoma Panhandles as well as all of Southwestern Oklahoma was also present.[195] That afternoon, multiple rounds of intense supercells formed across this region and pushed eastward. One of the cells produced a destructive and deadly low-end EF3 tornado that tracked through Perryton, Texas, causing significant damage to a mobile home park and destroying multiple downtown and industrial buildings, killing at least three people, and injuring about 100 others.[196][197] Other tornadoes were confirmed in Oklahoma and Texas along with swath of wind and hail damage. Supercell thunderstorms also developed along the western part of Lake Erie and moved southeastward, spawning several tornadoes, including three that were rated EF2. One of these tornadoes caused considerable damage in the Point Place neighborhood in Toledo, Ohio.[198] Severe weather also continued to impact the Gulf Coast and Southeastern United States into the early morning hours of June 16, where many instances of damaging winds and large hail were reported along with isolated tornadoes.[199] Flash flooding in Pensacola, Florida, resulted from 9.23 in (234 mm) of rain in five hours, and strong winds blew a tree into a house, killing one person. The flooding triggered a flash flood emergency.[200] A couple of weak tornadoes touched down in the Delaware Valley while more weak tornadoes touched down in Texas, Florida, Mississippi, Alabama, and Virginia. By June 16, the storms had left 664,000 customers without power along the Gulf Coast.[201]
More rounds of severe storms occurred on June 17, including a powerful MCS that pushed through Northern and Central Oklahoma. Both the Oklahoma City and Tulsa metropolitan areas had widespread wind damage with the latter metropolitan area seeing wind gusts of up to 100 miles per hour (160 km/h) and multiple weak tornadoes. On June 18, more tornadoes were confirmed in Florida and Mississippi, including an EF3 tornado which caused significant damage in Louin, Mississippi, where at least one fatality and 20 injuries occurred.[202][203] Scattered tornadoes occurred across the Southeast on June 19 as well, including an EF2 tornado that injured six people in Moss Point, Mississippi. Overall, 87 tornadoes were confirmed during this outbreak sequence.[204]
June 20–26
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62 | 19 | 20 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0 |

More waves of tornadic activity struck across the Great Plains, Mississippi Valley, Southeastern and Northeastern United States the day after the previous outbreak sequence ended. On the evening of June 21, a high-end EF3 tornado struck the western portion of Matador, Texas, resulting in devastating damage, four fatalities, and 15 injuries. Homes along the path of the tornado were leveled or swept completely away, with debris scattered across fields. Businesses were also flattened, trees were debarked and snapped off, and severe ground scouring was documented. Extreme damage to vehicles occurred along the path of the tornado, with cars being thrown long distances and completely mangled.[205] On June 22, two EF1 tornadoes touched down in Colorado and North Carolina. A high end EF1 tornado touched down in Highlands Ranch, a major suburb of Denver.[206][207] A severe hailstorm also moved through the Denver metropolitan area, which resulted in nearly 100 injuries at the Red Rocks Amphitheater before a concert.[208] Severe weather in Colorado forced a Major League Soccer game between the Colorado Rapids and Vancouver Whitecaps to be postponed.[209] A severe squall line also led to a record wind gust at George Bush Intercontinental Airport in Houston of 97 mph (156 km/h), surpassing the record from Hurricane Ike.[210] The outbreak continued into June 23 with more tornadoes being reported in Wyoming, Oklahoma and Colorado, including an EF3 tornado that caused significant damage near Granada. An EF2 tornado in Nebraska also prompted the issuance of tornado emergency for Scottsbluff and Gering.[211] More tornadoes touched down over Minnesota and Iowa on June 24, including an EF2 tornado that passed just east of Mahnomen, Minnesota. Several strong tornadoes occurred the next day in Indiana and Kentucky, including a deadly EF2 tornado that struck Rusk, Indiana, killing one person and injuring another. A total of 113 tornadoes touched down in the outbreak sequence along with five tornadic deaths, three non-tornadic deaths, and over 120 injuries.[212]
July 12
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

In the early morning, a squall line moved through Nebraska and Iowa producing a few tornadoes, including an EF2 tornado that tore the roof off of a home south of Logan, Iowa. Later in the day, the Storm Prediction Center issued a 10% chance of significant tornadoes for northern Illinois, including Chicago. A low-precipitation supercell produced a photogenic, but damaging high-end EF1 tornado that moved through the Chicago suburbs of Burr Ridge, Countryside, Hodgkins, McCook, Lyons and Stickney, snapping power lines and collapsing the roof and exterior walls of a motel.[213][214] A particularly dangerous situation tornado warning was issued for Chicago in result of this tornado.[215] Twin tornadoes also touched down near Elgin, Illinois, one of which was rated EF1 while the other was rated EF0.[216][217] The storms resulted in 172 flights being cancelled and over 550 flights delayed from Chicago O’Hare International Airport.[218]
July 19
[edit]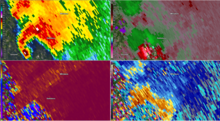
An intense multiple-vortex tornado touched down southwest of Dortches, North Carolina, leaving power poles bent and trees snapped. The tornado then crossed I-95, producing widespread tree damage and shutting down parts of the highway for several hours.[219] As it moved into the city limits of Dortches itself, it strengthened to high-end EF2 intensity, destroying multiple single-wide mobile homes and snapping power poles. The tornado then reached the north side of Rocky Mount after continuing to travel east-northeast, in which it encountered a residential building and collapsed every exterior wall. The tornado later advanced into Belmont Lake Golf Club, where it strengthened to mid-range EF3 intensity. The tornado collapsed a metal transmission tower and caused significant damage to a Pfizer warehouse facility, flipping and destroying nearby semi-trailer trucks. The tornado then weakened slightly as it crossed into Edgecombe County before lifting east of Battleboro.[220]
The tornado's peak estimated wind speeds were 150 mph (240 km/h), with a peak width of 600 yards (550 m) and a total path length of 16.5 miles (26.6 km).[220] It caused sixteen injuries, two of them resulting in hospitalization, but no fatalities. 38 homes were damaged. The National Weather Service office in Raleigh did not issue a tornado warning for the storm until the tornado had already been down for six minutes, resulting in scrutiny from some meteorologists on social media, but the National Weather Service defended the warning process and noted that the eventual warning came before the tornado dealt its most significant damage.[221] After law enforcement reported that up to 50,000 pallets of medicine had been damaged at the Pfizer facility, Erin Fox of the University of Utah Health said the damage could lead to shortages of certain drugs while the company deals with the situation.[222] FDA Commissioner Robert Califf later announced that, since hospitals already had the drugs or the drugs were on their way, no significant supply impacts were expected. Pfizer said as the tornado had damaged storage areas but not production equipment, any shortages would be less serious.[223] The tornado caused over $300 million (2023 USD) in damage.[224]
August 4-8
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 15 | 17 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |

On August 4, an EF2 tornado directly hit the town of Baring, Missouri, inflicting widespread damage to homes, trees, and other structures while injuring two people. Two days later, on August 6, a large and long-tracked EF2 tornado hit north of Pawnee, Illinois in Sangamon County, damaging or destroying homes and outbuilding before dissipating near Assumption in Christian County, almost an hour after touching down. On August 7, a high-end EF2 tornado hit the western suburbs of Knoxville, Tennessee. As the storm system brought hundreds of damaging wind reports throughout the Northeastern United States on August 7,[225] an intense, low-end EF3 tornado progressed through southern Lewis County, New York, striking the town of Lewis, and causing significant damage at the Snow Ridge Ski Resort at the end of its 16 miles (26 km) track near Turin, New York.[226] On August 8, an EF3 tornado touched down near Yuma, Colorado, where buildings and structures were significantly damaged or destroyed in Yuma County.[227][228][229]
August 18
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Multiple tornadoes impacted portions of southern New England on the morning of August 18. Three tornadoes touched down in Massachusetts, an EF1 tornado touched down in Connecticut, and an EF2 tornado lifted a car on I-295 near Scituate, Rhode Island.[230] This became the first F2/EF2 tornado in the state since 1986.[231] Flooding from the system also shut down I-91 in Connecticut, and a nearby hotel parking lot flooded.[232] Flooding also resulted in standing water along the Grand Central Parkway and Long Island Expressway in Queens.[233]
August 24-25
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 12 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A severe weather and tornado outbreak occurred across parts of the Great Lakes region and southwestern Ontario during the evening hours of August 24, including in the Grand Rapids and Webberville, Michigan areas, as well as in Metro Detroit. Near Webberville, an EF2 tornado prompted a PDS tornado warning, flipping cars and trapping people in their vehicles on I-96, resulting in two fatalities and four injuries, and causing $75 million in damage.[234][74][235] Roofs and buildings collapsed across Kent County due to a high-end EF1 tornado that moved through portions of the county.[236] An EF2 tornado also struck Fayette County, Pennsylvania early on August 25 as well.[237] Another person was killed in Michigan when a tree fell on a home in Lansing.[238] The storms also resulted in over 700,000 customers losing power in the Great Lakes area,[239] while another 20,000 customers lost power in Ontario.[71] Between the two nations, estimated economic losses reached $880 million.[240]
October 11-12
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A large storm system moved through Florida, spawning several tornadoes. In the early morning hours of October 12, a waterspout offshore of Clearwater Beach moved northeast and made landfall in Dunedin, partially tearing the roof off of an apartment building and earning a low-end EF2 rating. Soon after, another strong EF2 tornado moved through Crystal River, tearing the roof off of one home and collapsing an exterior wall. Later in the morning, another low-end EF2 tornado touched down in Palm Coast, unroofing one home and flipping a car. Four other EF0 tornadoes were also confirmed during this event.[78]
December 9-10
[edit]| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 |

A severe weather and tornado outbreak impacted portions of the Southern United States on December 9, especially in the state of Tennessee.[241] An EF1 tornado impacted portions of Weakley County, Tennessee, including in Sharon and Dresden and causing three injuries,[242] before impacting parts of Rutherford and across Gibson County, Tennessee, causing significant damage.[242][243] An EF3 tornado struck the northwestern part of Clarksville, Tennessee, among other surrounding areas in Tennessee and Kentucky.[244][245] Three people were killed, 62 others were injured, and at least 20,000 people were left without power.[246] A strong EF2 tornado prompted a tornado emergency to be issued for Hendersonville and Gallatin, Tennessee after it struck Madison in northern Nashville, where heavy damage occurred and three fatalities occurred.[247] The tornado also injured three other people elsewhere.[248][249][250][251] More tornadoes occurred on the next day, including an EF1 tornado in Wake County, North Carolina, west of Garner.[252] In all, 18 tornadoes touched down during the outbreak.[78]
Oceania
[edit]Australia
[edit]On December 12, a tornado was confirmed by the Bureau of Meteorology in the Australian town of Millicent as storms tore across South Australia. The tornado uprooted trees, damaged properties, and downed power lines.[253]
South America
[edit]Brazil
[edit]July 12
[edit]A long-tracked storm struck Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil on July 12, causing severe damage along a path of about 112 kilometres (70 mi). The storm produced at least one tornado, most likely a tornado family during this long track. At least EF2 vegetation damage was documented, with the most severe damage noted in the town of Sede Nova, which was struck by a tornado.[254]
October 4
[edit]A strong tornado developed in southern Brazil, affecting the city of Cascavel, Paraná. Roofs and trees suffered significant damage and a building was completely destroyed. The tornado has been given a F2 rating by SIMEPAR.[255]
See also
[edit]- Weather of 2023
- Tornado
- List of tornado outbreaks
- List of F5 and EF5 tornadoes
- List of F4 and EF4 tornadoes
- List of North American tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of 21st-century Canadian tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of European tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks in Asia
- List of Southern Hemisphere tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes striking downtown areas of large cities
- List of tornadoes with confirmed satellite tornadoes
- Tornado intensity
References
[edit]- ^ "Storm Event Database: U.S. Tornadoes January—August". National Centers for Environmental Information. Retrieved 15 December 2023.
- ^ "Annual Severe Weather Report Summary 2023". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on January 9, 2023. Retrieved January 9, 2023.
- ^ NWS Storm Prediction Center [@NWSSPC] (1 February 2023). "January 2023 was an active tornado month. Preliminarily, 126 tornadoes have been confirmed, which is the 3rd most on record. https://t.co/PtEmxagWOW" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 22 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "February Month in Review". Facebook. NOAA NWS Storm Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 11 March 2023. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ Livingston, Ian (6 April 2023). "Tornado deaths in 2023 are already more than double last year′s total". Washington Post. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ Pieter Groenemeijer (ESSL); Lothar Bock (DWD); Juan de Dios Soriano (AEMet); Maciej Dutkiewicz (Bydgoszcz University of Science and Technology); Delia Gutiérrez-Rubio (AEMet); Alois M. Holzer (ESSL); Martin Hubrig; Rainer Kaltenberger; Thilo Kühne (ESSL); Mortimer Müller (Universität für Bodenkultur); Bas van der Ploeg; Tomáš Púčik (ESSL); Thomas Schreiner (ESSL); Miroslav Šinger (SHMI); Gabriel Strommer (ESSL); Andi Xhelaj (University of Genova) (30 July 2023). "The International Fujita (IF) Scale" (PDF). European Severe Storms Laboratory. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ Shige, Dalian (April 16, 2023). "Shandong, Lizhuang Town, Tancheng County, Linyi encountered the strongest tornado". k.sina.com. Sina. Retrieved April 21, 2023.
- ^ "Terrifying tornado rips through Chinese city, leaving destruction in wake". newsflare.com. Newsflare. April 15, 2023. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- ^ "Tornado over 100 km/h winds strikes China! Storm in Shandong causing major damage". youtube.com. Unstoppable Weather. April 16, 2023. Retrieved April 21, 2023.
- ^ "Incredible close up vid, however this was a different tornado in northern Shandong Province, we might deal with a tornado outbreak today". Twitter. Retrieved 16 April 2023."Tornado in Linyi, Shandong Province this afternoon! ! We've confirmed this one has already caused severe damage, however the damage extent remains unknown". Twitter. Retrieved 16 April 2023."Insane home video of the powerful tornado which blasted thru Linyi, Shandong Province. Major damage observed with some injuries reported, cars and tractors were tossed, transmission tower was down". Twitter. Retrieved 16 April 2023."woah, looks like some intense damage from the Linyi, Shandong Province tornado today, an EF2 rating was definitely possible". Twitter. Retrieved 16 April 2023."Strong tornado yesterday in TanCheng, Shandong Province in China". Twitter. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ^ "百度安全验证". wappass.baidu.com. Retrieved 2023-06-04.
- ^ @Ericwang1101 (June 2, 2023). "Tractor thrown and damaged after the Fuxin tornado yesterday..." (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ @Ericwang1101 (June 2, 2023). "This is what it looks like after the Kaiyuan tornado yesterday..." (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Yong, Wu (June 1, 2023). "Tornado hits Liaoning province". chinadaily.com. China Daily. Retrieved June 3, 2023.
- ^ @Ericwang1101 (June 1, 2023). "Large, violent tornado in Fuxin, Liaoning Province hours ago, this deadly tornado moved directly into the city, literally a carbon copy of the Kaiyuan EF4" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ @yangyubin1998 (June 1, 2023). "Up to now, the tornado has injured nearly 20 people, but luckily no one died" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Wang, Eric (22 July 2023). "An old but fresh news, local weather bureau just confirmed an EF2 tornado in Danzhou, Hainan Province on 7/17, this tornado was spawned by Typhoon #Talim". Twitter. @EricWang1101. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ Eric Wang (13 August 2023). "Confirmed EF2 tornado in Yancheng, Jiangsu Province this afternoon, unfortunately there're reported two fatalities with 15 injuries furthermore, 283 residences damaged or destroyed for a rough estimate.This is the first killer tornado in China and Jiangsu Province since 7/20/2022". Twitter. @Ericwang1101. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- ^ @Ericwang1101 (August 13, 2023). "Tornado in Yancheng, Jiangsu Province this afternoon as it churning across the field, intense rotation with debris scattered, confirmed injuries and house damage" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "Deadly tornado strikes Longgang and Jiulongkou villages in Dafeng District, Yancheng City, at least 2 fatalities and 15 injuries reported". Dimsum Daily Hong Kong. August 13, 2023. Retrieved August 13, 2023.
- ^ Michel, Deeandra (20 September 2023). "AP: Tornadoes Kill 10 People And Seriously Injure 4 Others In Eastern China". WCCB. AP News. Archived from the original on 20 September 2023. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
- ^ Zhang, Mengchen (September 20, 2023). "10 dead after tornadoes tear through two cities in eastern China". CNN. Retrieved September 20, 2023.
- ^ Wang, Eric (20 September 2023). "Wtf! Jiangsu weather bureau just confirmed an EF3 tornado hit Funing last night, this is the strongest tornado ever recorded since 2016 Funing EF4 in Jiangsu Province.Houses completely destroyed, farmlands scoured, trees debarked, this tornado was responsible for 5 fatalities" (Post on 𝕏). 𝕏. @Ericwang1101. Archived from the original on 20 September 2023. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
- ^ Wang, Eric (20 September 2023). "Major brick residence damage in Funing during last night EF3 tornado. one of the hardest hit village, Banhu village was hit by the powerful EF4 tornado seven years ago, what a coincidence! This tornado has already led to five fatalities" (Post on 𝕏). 𝕏. @EricWang1101. Archived from the original on 20 September 2023. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
- ^ Kala, Chhabi (March 25, 2023). "Tornado in Punjab's Fazilka damages houses, crops". indiatoday.in. India Today. Retrieved April 21, 2023.
- ^ Vortix [@VortixWx] (24 March 2023). "Todays #tornado that struck Fazilka, #India looks to have caused some fairly significant damage. local news station reported that "multiple people were trapped under debris and 50 homes blown away" #wxtwitter #wxindia https://t.co/nGiS1WB6T2" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 25 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Wang, Eric [@Ericwang1101] (24 March 2023). "Dalton, but India version https://t.co/NESMWEUTho" (Tweet). Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "UPDATE Korban Puting Beliung di Kodi Sumba Barat, 9 Orang Meninggal, 21 Rumah Rusak". Pos-kupang.com (in Indonesian). April 30, 2023. Retrieved June 10, 2023.
- ^ Ali, Felixianus (April 30, 2023). "NTT Dilanda Puting Beliung Korban Meninggal 9 Orang dan 21 Rumah Rusak Berat di Kodi Sumba Barat Daya - Insiden 24". NTT Dilanda Puting Beliung Korban Meninggal 9 Orang dan 21 Rumah Rusak Berat di Kodi Sumba Barat Daya - Insiden 24 (in Indonesian). Retrieved June 10, 2023.
- ^ "Eight killed, more than 100 injured as Tornado hit Leiway Township in Nay Pyi Taw". Eleven Media Group Co., Ltd. Retrieved 2023-04-22.
- ^ "Rare big tornado near Myanmar capital kills 8". abcnews.go.com. ABC News. April 22, 2023. Retrieved April 29, 2023.
- ^ "Rare Massive Tornado hits Oman". 24 April 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "Tornado and thunderclouds hit this part of Oman". www.timesofoman.com. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "Large tornado hits Taif, Saudi Arabia". The Watchers. 14 March 2023. Archived from the original on 14 March 2023. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- ^ "تقف على موقع إعصار الطائف وترصد الأضرار". okaz.com. Okaz. March 13, 2023. Archived from the original on March 17, 2023. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ a b c "European Severe Weather Database". eswd.eu. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ^ "European Severe Weather Database".
- ^ a b c d e f g "European Severe Weather Database". ESWD. European Severe Storms Laboratory. Retrieved 4 November 2023.
- ^ "European Severe Weather Database".
- ^ https://eswd.eu/cgi-bin/eswd.cgi
- ^ "Tornade EF2 à Pontarion (Creuse) le 9 mars 2023. Tornade dans la Creuse (23), région Nouvelle-Aquitaine. Tornade F2 en France. KERAUNOS - Observatoire Français des Tornades et des Orages Violents". Archived from the original on 2023-03-25. Retrieved 2023-03-25.
- ^ "Tornade dans la Creuse le 9 mars" (in French). French Observatory of Tornadoes and Violent Thunderstorms (Keraunos). Archived from the original on 9 March 2023. Retrieved 9 March 2023.
- ^ "European Severe Weather Database". European Severe Storms Laboratory. Archived from the original on 20 September 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2023.
- ^ https://eswd.eu/cgi-bin/eswd.cgi
- ^ "Tornade EF2 à Juvigné (Mayenne) le 17 septembre 2023". Keraunos (in French). French Observatory of Tornadoes and Violent Thunderstorms. 5 October 2023. Archived from the original on 6 October 2023. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- ^ a b c d "European Severe Weather Database". European Severe Storms Laboratory. Archived from the original on 20 September 2022. Retrieved 20 January 2023.
- ^ "[F1] Hinte, NI - 01.02.2034". TornadoMap.org. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ "[F2] Lashorst, NW". TornadoMap.org. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ "Lashorst 01.02.2023". Tornadoliste Deutschland. Archived from the original on 5 February 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20230923045731/https://eswd.eu/cgi-bin/eswd.cgi?lang=en_0&lastquery=4534776276
- ^ https://eswd.eu/cgi-bin/eswd.cgi
- ^ https://twitter.com/BarryWhyte85/status/1733846088275132917
- ^ https://www.leitrimobserver.ie/news/local-news/1368795/watch-dramatic-footage-of-leitrim-village-tornado.html
- ^ "AIR TRACK: DAMAGE TO HOMES AND INFRASTRUCTURE. THE STATE OF DISASTER WILL BE ASKED". Facebook. Città di Valmontone. Archived from the original on 4 March 2023. Retrieved 20 January 2023.
- ^ "July 22, 2023 Alfonsine, Italy IF3 Tornado (ESWD)". European Severe Weather Database. European Severe Storms Laboratory. July 2023. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ Korošec, Marko (2 August 2023). "A rare tornado strikes the town of Ilirska Bistrica, Slovenia, today, Aug 1st, 2023. Significant damage reported". Severe-weather.eu. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ "Met4Cast. on X". X (formerly Twitter). Retrieved 2023-11-05.
- ^ https://twitter.com/TorroUK/status/1721547810280022090
- ^ Tomšič, Matic (2 August 2023). "Posnetek iz zraka: poglejte razdejanje po tornadu v Ilirski Bistrici". Siol.net (in Slovenian). Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ Korošec, Marko (2 August 2023). "A rare tornado strikes the town of Ilirska Bistrica, Slovenia, today, Aug 1st, 2023. Significant damage reported". Severe-weather.eu. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ "Reported tornado leaves trees down, windows smashed and up to 20 cars damaged in Littlehampton". ITV. September 18, 2023. Retrieved September 21, 2023.
- ^ Jolly, Bradley (September 18, 2023). "Met Office gives update after 'mini-tornado' strikes south coast amid storms". Daily Mirror. Retrieved September 21, 2023.
- ^ "Littlehampton-Lyminster tornado, Sunday 17th September 2023". The Tornado and Storm Research Organisation. Retrieved September 22, 2023.
- ^ https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-england-sussex-67254819
- ^ https://eswd.eu/cgi-bin/eswd.cgi
- ^ a b "Didsbury AB Tornado an EF4". Northern Tornadoes Project. July 4, 2023. Retrieved July 4, 2023.
- ^ Markus, Jade (July 2, 2023). "Alberta tornado witness says twister hit homes leaving damage, gas 'spewing' and power lines down". CBC. Retrieved July 2, 2023.
- ^ Northern Tornadoes Project [@westernuNTP] (July 2, 2023). "Two NTP survey teams will be investigating the damage caused by a powerful tornado in the Didsbury, AB area yesterday. An NTP team captured this image of the ground scour track going off into the distance last evening. They are coordinating with @ECCCWeatherAB who are also on the scene. #ABstorm" (Tweet). Retrieved July 2, 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Two tornadoes with wind speeds of 155 km/h touched down in Ottawa on Thursday". Ottawa. 2023-07-15. Retrieved 2023-07-17.
- ^ "PHOTOS: Quebec cleans up after storms bring tornado, torrential rain". Yahoo News. 2023-07-14. Retrieved 2023-07-17.
- ^ a b MacLeod, Brian (28 August 2023). "Two tornadoes touched down in Windsor area Aug. 24". Windsor Star. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Tornado in Windsor ON on Aug 24". www.uwo.ca. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Tornado in Tecumseh ON on Aug 24". www.uwo.ca. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ a b Wolfe, Elizabeth (2023-08-25). "Vehicles overturned by suspected tornado along I-96 as severe storms batter Michigan, leaving more than 330,000 without power". CNN. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ^ "Q3 Global Catastrophe Recap October 2023" (PDF). Aon Benfield. Retrieved October 31, 2023.
- ^ "NWS Damage Survey for 07/16/2023 Tornado Event Aguada". Iowa Environmental Mesonet. National Weather Service in San Juan, Puerto Rico. 17 July 2023. Archived from the original on 18 July 2023. Retrieved 18 July 2023.
- ^ "Annual U.S. Killer Tornado Statistics". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on January 14, 2023. Retrieved January 15, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "Damage Assessment Toolkit". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 23 April 2020. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ "NWS Damage Survey for Jessieville Tornado Event". Iowa State University, Iowa Environmental Mesonet. January 3, 2023. Archived from the original on January 4, 2023. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ Staff (January 2, 2023). "UPDATE: Two J'ville staff members suffered minor injuries m; school closed Tuesday". The Sentinel-Record. Archived from the original on January 2, 2023. Retrieved January 3, 2023.
- ^ "SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Monday January 02, 2023". NOAA's National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 3 January 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". NOAA's National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 4 January 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ 'I've never seen anything like it': Severe weather plagues South with flooding rainfall, tornadoes Archived 2023-01-04 at the Wayback Machine, AccuWeather, January 4, 2023
- ^ Damaging weather menaces the Southeast as a 'brutal' storm system threatens California with fresh flooding Archived 2023-01-05 at the Wayback Machine, WSVN, January 4, 2023
- ^ Amtrak Alerts [@AmtrakAlerts] (3 January 2023). "City of New Orleans Train 59, which departed Chicago (CHI) on 1/2, is being delayed between Fulton (FTN) and Memphis (MEM) due to flash flood warnings" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 7 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Amtrak Alerts [@AmtrakAlerts] (3 January 2023). "UPDATE: the City of New Orleans Train 59, which departed Chicago (CHI) on 1/2 continues to be delayed north of Fulton (FTN) due to flash flooding and debris on the tracks" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 4 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Amtrak Alerts [@AmtrakAlerts] (3 January 2023). "UPDATE: the City of New Orleans Train 59 which departed Chicago (CHI) on 1/2 has arrived into Fulton (FTN) 3hrs 40mins late. Further delays are expected due to a flood warning in the area. Updates to follow as more information becomes available" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 27 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Ground stop at MSP Airport now lifted after heavy snow and ice Tuesday, Fox 9 Minneapolis, January 3, 2023
- ^ Minnesota weather: Huge January snowstorm among the largest on record for Twin Cities, Fox 9 Minneapolis, January 5, 2023
- ^ 1 killed in Wright County crash; driving conditions remain slick for much of the state, Kare1, January 3, 2023
- ^ "BMX Tornado Warning #28". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. National Weather Service Birmingham AL. Archived from the original on 1 September 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2023."BMX Tornado Warning #29". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. National Weather Service Birmingham AL. Archived from the original on 1 September 2020. Retrieved 12 January 2023."BMX Tornado Warning #30". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. National Weather Service Birmingham AL. Archived from the original on 12 January 2023. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ "TIMELINE: Seven dead, dozen missing in Autauga County after tornado hits central Alabama". Montgomery Advertiser. Archived from the original on 13 January 2023. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ "SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Wednesday, January 11, 2023". NOAA's National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 12 January 2023. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ "Tornado hits Selma, Alabama; 7 deaths reported across South". KOLD News13. Archived from the original on January 13, 2023. Retrieved January 13, 2023.
- ^ a b National Weather Service in Tallahassee, Florida (January 23, 2023). NWS Damage Survey for 01/22/2023 Tornado Event (Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. Archived from the original on January 24, 2023. Retrieved January 23, 2023.
- ^ NWS Houston [@NWSHouston] (25 January 2023). "NWS Houston can now confirm that the Deer Park/Pasadena tornado will be preliminarily rated EF3, with an estimated maximum path length of 18 mi, maximum path width of 0.66 mi, and maximum wind speed of 140 mph. We will provide a full summary later this evening. #houwx #txwx" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 15 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "HGX Tornado Warning #8". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. National Weather Service Houston/Galveston TX. Archived from the original on 1 September 2020. Retrieved 24 January 2023.
- ^ Stewart, Nick [@NStewCBS2] (24 January 2023). "According to NWS Houston, this is was the first ever #tornado emergency product issued by the office" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". NOAA's National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 24 January 2023. Retrieved 24 January 2023.
- ^ "Texas Event Report: EF3 Tornado". National Centers for Environmental Information. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ^ "Three injured, hospitalized in Louisiana after mobile homes were hit by the tornado, sheriff says". The Advocate. 24 January 2023. Archived from the original on 25 January 2023. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ^ NWS Houston [@NWSHouston] (25 January 2023). "Here are the preliminary rainfall totals over the past 24 hours. A record rainfall of 4.05" was set at the City of Houston yesterday. This breaks the old record of 1.94" set in 2011. More detailed rainfall totals across SETX 👉https://t.co/M3DFlTFlY4 #houwx #glswx #bcswx #txwx https://t.co/AW3mHbnybI" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Road closed due to flood waters hours after heavy rain, CW39, January 25, 2023
- ^ "National Weather Service confirms tornado in Searcy County, Ark. on Thursday morning". KY3. 16 February 2023. Archived from the original on February 17, 2023. Retrieved February 17, 2023.
- ^ Two-sided storm unleashes heavy snow, tornadoes and flooding Archived 2023-02-19 at the Wayback Machine, AccuWeather, February 18, 2023
- ^ USA – Fatalities After Floods in Kentucky and West Virginia Archived 2023-02-21 at the Wayback Machine, FloodList, February 19, 2023
- ^ Interstate 65 reopens after roadway floods briefly near Cullman Archived 2023-03-20 at the Wayback Machine, WBRC News, February 16, 2023
- ^ NJ Tornado Confirmed, Marking State's 5th February Twister Since 1950, State 4 NY, February 22, 2023
- ^ Rare February tornado that spun through New Jersey rated EF-2, Fox Weather, February 21, 2023
- ^ EF2 Tornado Strikes Mercer County, NJ, as Storms Leave Damage in Several Places, NBC Philadelphia
- ^ Rare EF2 tornado confirmed after heavy damage in New Jersey, AccuWeather, February 22, 2023
- ^ At least 75 displaced by Mercer County storms, police say, CBS Philadelphia, February 22, 2023
- ^ "Derecho, Tornadoes Leave Damage Across Southern Plains | Weather.com". The Weather Channel. Archived from the original on 2023-02-27. Retrieved 2023-02-28.
- ^ "SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Sunday February 26, 2023". www.spc.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 2 March 2023. Retrieved 27 February 2023.
- ^ "Tornadoes tear through Oklahoma City area; gust reaches 114 mph in Texas as severe storms sweep across Plains". www.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 2023-02-27. Retrieved 2023-02-27.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 27 February 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Mar 1, 2023, 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook". www.spc.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 2023-03-05. Retrieved 2023-03-05.
- ^ herzmann, daryl. "IEM :: PNS from NWS LZK". mesonet.agron.iastate.edu. Archived from the original on 2023-03-04. Retrieved 2023-03-05.
- ^ US Department of Commerce, NOAA. "High Winds, Flooding, and Tornadoes - March 3, 2023". www.weather.gov. Archived from the original on 2023-03-05. Retrieved 2023-03-05.
- ^ Wolfe, Elizabeth (March 4, 2023). "At least 13 people are dead as severe storms bring tornadoes and flooding to South, now sweeps across Northeast". cnn.com. CNN. Archived from the original on March 5, 2023. Retrieved March 6, 2023.
- ^ NWS Los Angeles [@NWSLosAngeles] (23 March 2023). "**MONTEBELLO UPDATE** Our damage survey team has officially confirmed that there was a TORNADO in Montebello around 11:20 AM on 3/22/23. No EF rating yet, we are still assessing the damage! A full report will be coming late this evening. EF Scale: https://t.co/VWCYSkHMN6" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 27 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ Kiszla, Cameron (March 22, 2023). "'Craziest thing I've ever seen': Tornado damages buildings in Montebello". ktla.com. KTLA. Archived from the original on March 23, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2023.
- ^ Witnesses detail moments tornado swept through Montebello. KCAL News. 23 March 2023. Archived from the original on 23 March 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2023 – via YouTube.
- ^ See How Much Rain Has Fallen in LA and Where Rainfall Records Were Broken, NBC Los Angeles, March 22, 2023
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 25 March 2023. Retrieved 25 March 2023.
- ^ McDuffie, Will (25 March 2023). "At least 19 dead in 'destructive' Mississippi tornado strike, officials say". abcNEWS. Archived from the original on 25 March 2023. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- ^ Masih, Niha; Bisset, Victoria; Suliman, Adela; Bella, Timothy; McDaniel, Justine. "Tornadoes kill 24 in 100-mile path through Mississippi, Alabama". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on March 25, 2023. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- ^ "12 tornadoes confirmed in Illinois, including near Belvidere Apollo Theatre roof collapse, NWS says". April 2023. Archived from the original on 2023-04-01. Retrieved 2023-04-01.
- ^ "Widespread damage in Whiteland from storm". 31 March 2023. Archived from the original on 2 April 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
OHXSUMwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ National Weather Service in Huntsville, Alabama (April 1, 2023). NWS Damage Survey for 4/1/2023 Tornado Event (Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ^ Reports of damage after severe storms moved through the Tennessee Valley (Report). WHNT. April 1, 2023. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|agency=ignored (help) - ^ a b NWS Damage Surveys for April 1, 2023 Tornado Outbreak and Wind Event - Update 10 (Report). April 7, 2023. Retrieved April 7, 2023 – via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|agency=ignored (help) - ^ Kiefer, Paul (April 2, 2023). "Sussex County begins recovery from Saturday tornado". Delaware Public Media. Retrieved April 3, 2023.
- ^ Tanyos, Faris (April 1, 2023). "One killed after tornado strikes Delaware; severe weather slams Northeast". CBS News. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ^ National Centers for Environmental Information (July 2023). "U.S. Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters (1980-2023)" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ^ Oberholtz, Chris (5 April 2023). "Rescue efforts underway in rural Missouri towns after strong tornado reported". FOX Weather. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ^ Heller, Marsha (5 April 2023). "At least 5 dead, multiple injured after tornado hits parts of Bollinger County". KFVS12. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ^ "Preliminary report on the tornadoes of Wed., April 5". www.weather.gov. NOAA. Retrieved 2023-04-07.
- ^ "Early April Midwest, Mid-Mississippi Valley Severe Weather Outbreak (RECAP)". The Weather Channel. April 7, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ Vogt, Dustin (April 6, 2023). "Louisville man killed by falling tree during storms identified". WAVE. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ^ Cubs-Reds postponed; rescheduled as split DH on 9/1, MLB.com, April 5, 2023
- ^ Ground stop ordered for Chicago airports impacting flights at Dayton International Airport, WHIO, April 5, 2023
- ^ Thursday's Mets home opener postponed to Friday, MLB.com, April 5, 2023
- ^ Phillies Postpone Thursday's Home Opener Due to Expected Storms, NBC 10 Philadelphia, April 5, 2023
- ^ Orioles’ home opener against Yankees postponed to Friday, WTOP, April 6, 2023
- ^ a b c d e "Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters". National Centers for Environmental Information. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- ^ "April 15, 2023 Tornadoes". weather.gov. NWS St. Louis, MO. April 16, 2023. Retrieved April 30, 2023.
- ^ Royals-Braves games delayed due to inclement weather, Fox4KC, April 15, 2023
- ^ "The Severe Weather and Tornado Outbreak of April 19, 2023". www.weather.gov. Archived from the original on 21 April 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 4/19/23 TORNADO EVENT - UPDATE #3". National Weather Service. 27 April 2023. Retrieved 27 April 2023."April 19, 2023 Large Hail & Tornado Event". ArcGIS StoryMaps. National Weather Service Norman OK. 28 April 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ Douglas, Kaylee (21 April 2023). "NWS: 12 tornadoes touched down across Oklahoma during April 19 storms". KFOR.com Oklahoma City. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ "Five Oklahoma tornado tracks identified by National Weather Service, so far". The Oklahoman. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ Leffler, Thomas (April 20, 2023). "At least 3 dead after damaging EF3 tornado levels homes in Oklahoma". AccuWeather. Retrieved April 21, 2023.
- ^ "Tornadoes threaten Blanchard, Cole; severe thunderstorms, hail persist across OKC area". The Oklahoman. Retrieved 2023-04-20.
- ^ Withrow, Brooke (2023-04-20). "Tornado touches down in Cole as severe weather moves across Oklahoma". KOCO. Retrieved 2023-04-20.
- ^ "Live: Tornadoes cause widespread damage in Oklahoma". KFOR.com Oklahoma City. 2023-04-19. Retrieved 2023-04-20.
- ^ "Watch live: Tornadoes cause damage in central Oklahoma". News on 6. April 19, 2023.
- ^ a b "10:40 AM Preliminary update on several ongoing damage surveys. We have found EF0 damage just south of Tinker. We have also found EF1-EF2 type damage near Cole and near Etowah. The surveys are just beginning and will take some time to complete. #okwx Please be patient with us". Twitter. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "9:51pm - THIS IS ANOTHER CASE OF THE STORM HAVING ERRATIC BEHAVIOR. THE STORM IS EXHIBITING A FUJIWARA EFFECT, WITH THE CIRCULATIONS ROTATING AROUND EACH OTHER. DO NOT ANTICIPATE STORM MOTION, TAKE COVER IF YOU'RE IN THE WARNING. #okwx". Twitter. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Jonathan Greco (April 20, 2023). "Oklahoma Baptist University sees extensive damage during severe weather, tornado outbreak". KOCO-TV.
- ^ "Hail Size of 'Brick' Knocks Out Bob Mills SkyNews 9 Helicopter Windshield". KWTV-DT. Griffin Media. April 20, 2023.
- ^ "Tornado Damages Osage SkyNews 6". KOTV-DT. Griffin Media. April 20, 2023.
- ^ "One of the news stations lost a chopper yesterday. Shawnee Airport has some hangars that are just GONE now. They said chopper totaled". Twitter. April 20, 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ "Tornado Touches Down in Tyler, Texas". MSN. 24 April 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ "Federal disaster assistance requested following Oklahoma's tornado outbreak". MSN. 24 April 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ "April 19 Severe Weather Event: April 22 Situation Update 4" (Press release). Government of Oklahoma. April 22, 2023. Retrieved June 4, 2023.
- ^ Parts of Connecticut were in moderate drought or abnormally dry. Did recent downpours end it?, Hartford Courant, April 25, 2023
- ^ "National Weather Service data shows NYC rainfall totals for weekend storm". Silive. April 23, 2023. Retrieved July 16, 2023.
- ^ Finch, Allison (April 25, 2023). "'Horrible tragedy': Weekend storms kill 2 children in the Northeast". accuweather.com. AccuWeather. Retrieved May 1, 2023.
- ^ Severe thunderstorms, tornadoes possible along East Coast, including I-95 corridor, on Sunday, Fox Weather, April 30, 2023
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center 20230505's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center 230506's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- ^ After rain delay, Taylor Swift rocks Nashville: Top moments from the shows, USA Today, May 8, 2023
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 12 May 2023.
- ^ Ground stop at Denver International Airport amid hailstorm and tornado warnings, CBS News, May 10, 2023
- ^ "As of 9:32 pm CT, Heartland Flyer Train 822 is being delayed in Purcell (PUR) due to severe weather warnings". Twitter. Retrieved 17 May 2023."UPDATE: As of 11:34pm CT, Heartland Flyer Train 822 is on the move and currently operating approx. 2hr 40min late". Twitter. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ Denver just had one of its rainiest days ever, but a drier weekend awaits us, Denverite, May 12, 2023
- ^ Tornado seen near Uehling amid severe weather, retrieved 2023-05-13
- ^ "Huge wall of rain captured in Oakland, NE after possible tornado | Latest Weather Clips". Fox Weather. Retrieved 2023-05-13.
- ^ Tank vs. Tornado - Insane Intercept in Dominator 3 on YouTube
- ^ Breen, Kerry (13 May 2023). "1 dead, 10 hospitalized after tornado touches down in Laguna Heights, Texas". CBS NEWS. Retrieved May 13, 2023.
- ^ Barber, Katy (13 May 2023). "At least 1 dead after EF-1 tornado hits South Texas town, official says". mySanAntonio.com. Retrieved May 13, 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 13 May 2023.
- ^ "Tornado warning canceled for Madison County, Illinois". ksdk.com. May 13, 2023. Retrieved 2023-05-15.
- ^ Satre, Zane (2023-05-15). "What we know about the tornadoes and funnel clouds spotted throughout Iowa Saturday". KCCI. Retrieved 2023-05-15.
- ^ "Tornadoes touch down in Iowa Saturday afternoon". who13.com. 2023-05-13. Retrieved 2023-05-15.
- ^ "Ron DeSantis tiptoes around Iowa as Trump cancels visit amid tornado threat". NBC News. 14 May 2023. Retrieved 2023-05-15.
- ^ Donegan, Brian (June 14, 2023). "'Particularly Dangerous Situation' unfolding in South with 90-mph winds, tornadoes possible". FOX Weather. Retrieved June 14, 2023.
- ^ Tornado Captured Near Damascus, Georgia, retrieved 2023-06-15
- ^ "Multiple buildings destroyed and 7,600 people are without power in Cass County, Texas after tornado". MSN. Retrieved 15 June 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved June 15, 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Jun 15, 2023 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-06-16.
- ^ "Devastating tornado tears through Texas town, at least 3 dead, 100 injured". MSN. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ^ Shapiro, Emily; Golembo, Max; Griffin, Melissa. "Texas town devastated by tornado, 5 dead across South from severe weather". ABC News. Retrieved 2023-06-16.
- ^ "Damage from likely tornado reported in Point Place Thursday evening". wtol.com. June 15, 2023. Retrieved June 16, 2023.
- ^ "Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved June 16, 2023.
- ^ Flash Flood Emergency prompts water rescues in Pensacola, Florida, as foot of rain falls in hours, Fox Weather, June 16, 2023
- ^ Factbox: Storms leave over 664,000 without power along U.S. Gulf Coast, Reuters, June 16, 2023
- ^ "1 dead, at least 18 injured after tornado hits central Mississippi town - CBS News". www.cbsnews.com. June 19, 2023. Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- ^ Finch, Allison (June 19, 2023). "At least 1 dead, 20 injured following tornado in Louin, Mississippi". AccuWeather. Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- ^ Walker, Jude (2023-06-19). "Tornado Touches Down in Destin This Morning, Numerous Videos of it Captured". KPEL 96.5. Retrieved 2023-06-19.
- ^ "Violent Tornado Crosses Trough Madator,TX". TheWashingtonPost.com. June 21, 2023.
- ^ Medina, Eduardo (2023-06-22). "Storm Barrels Through Tiny Texas Town, Killing at Least 4". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2023-06-22.
- ^ Finch, Allison (June 22, 2023). "At least 4 dead following 'horrific' tornado in Matador, Texas". AccuWeather. Retrieved June 22, 2023.
- ^ Colorado amphitheater hail storm injures nearly 100 ahead of planned Louis Tomlinson concert, CNN, June 22, 2023
- ^ Major League Soccer match between Colorado and Vancouver postponed by severe weather, San Diego Tribune, June 22, 2023
- ^ Wind gust at Bush IAH clocked at 97 miles per hour during Wednesday's storm, KHOU, June 21, 2023
- ^ Scottsbluff, Nebraska Braces for Massive Tornado; Tornado Emergency Declared, BNN, June 23, 2023
- ^ "Indiana Tornadoes Leave At Least One Dead". abc7chicago.com. June 25, 2023.
- ^ "Storm damage from possible tornado at Joliet Ave & Lawndale in McCook @WGNNews". Twitter. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ "Survey team has completed the ground survey of the Burr Ridge to Stickney tornado. Preliminary rating of EF-1 with max winds near 110 mph. In addition to numerous trees snapped and uprooted, several businesses saw significant damage. More to come later. #ilwx". Twitter. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ "LOT Tornado Warning #25". Iowa Environment Mesonet. National Weather Service Chicago IL. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- ^ "The Kane County team has confirmed a second tornado in Elgin just to the south of the first tornado track. This tornado had a max intensity of EF-0 with max wind speed of 85 mph. The tornado began close to McDonald Rd and ended along Hopps Road. More info to come later". Twitter. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ "Survey Update: Our team working in Kane County confirms a tornado in Elgin with a maximum intensity EF-1 and maximum wind speed of 100 mph. The track roughly started east of Rt. 47 and ended near the railroad tracks west of Villa Olivia Golf Course. More info coming later. #ilwx". Twitter. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ Tornado swarm strikes Chicago area, forcing hundreds of flight cancellations at O’Hare, AccuWeather, July 13, 2023
- ^ Speck, Emilee; Yablonski, Steven; Wulfeck, Andrew; Sistek, Scott (July 20, 2023). "EF-3 tornado causes extensive damage to a Pfizer medicine processing facility in North Carolina". Fox Weather. Archived from the original on July 23, 2023. Retrieved July 24, 2023.
- ^ a b National Weather Service in Raleigh, North Carolina (July 20, 2023). "NWS Damage Survey for July 19, 2023 Tornado Event in Nash and Edgecombe Counties". Iowa Environmental Mesonet. Archived from the original on July 20, 2023. Retrieved July 24, 2023.
- ^ Wagner, Adam (July 20, 2023). "Authorities issued tornado warning for Eastern NC 6 minutes after storm hit the ground". News and Observer. Archived from the original on July 24, 2023. Retrieved July 24, 2023.
- ^ Lenthang, Marlene (July 19, 2023). "North Carolina tornado could lead to medication shortages after Pfizer plant was hit, expert warns". NBC News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on July 23, 2023. Retrieved July 24, 2023.
- ^ Schoenbaum, Hannah (July 21, 2023). "Tornado damage to Pfizer plant unlikely to cause major drug supply shortages, FDA says". Associated Press. Archived from the original on July 23, 2023. Retrieved July 24, 2023.
- ^ The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's finalized damage survey:
- National Centers for Environmental Information; National Weather Service (18 October 2023). "North Carolina Event Report: EF3 Tornado (Nash County)". Storm Event Database. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 18 October 2023. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- National Centers for Environmental Information; National Weather Service (18 October 2023). "North Carolina Event Report: EF3 Tornado (Edgecombe County)". Storm Event Database. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 18 October 2023. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ "SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Monday August 07, 2023". www.spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2023-08-09.
- ^ Staff (August 8, 2023). "EF3 tornado confirmed in Lewis County". 7 News/WWNY. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- ^ Cook, Lanie Lee (August 8, 2023). "'Extremely dangerous' tornado touches down in Yuma". FOX31 Denver/KDVR. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- ^ Case, Angela; Bianchi, Chris (August 8, 2023). "Eastern Plains hit by tornadoes, huge hail". 9 News/KUSA. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- ^ "2 tornadoes tear through Yuma County, destroying property - CBS Colorado". www.cbsnews.com. 2023-08-09. Retrieved 2023-08-10.
- ^ National Weather Service of Boston/Norton, MA (18 August 2023). "PRELIMINARY INFORMATION ON AUGUST 18 TORNADOES IN SOUTHERN NEW ENGLAND". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ Dube, Alex; Kurman, Josh (2023-08-19). "Strongest tornado since 1986 causes damage throughout Rhode Island". ABC6. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ^ Dempsey, Christine (2023-08-18). "Stormwater floods hotel, parking lots, cars near I-91 in Rocky Hill". CT Insider. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ^ "Strong thunderstorms cause short airport ground stops, flooded roadways, some power outages". abc7ny. 2023-08-18. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ^ National Centers for Environmental Information; National Weather Service (17 November 2023). "Michigan Event Report: EF2 Tornado (Ingham County)". Storm Events Database. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- ^ "Ingham County tornado upgraded to EF2, unknown number of people injured on I-96". Lansing State Journal. Retrieved 2023-08-26.
- ^ Tunison, John (2023-08-25). "Damage reported in West Michigan from storm, possible tornado". mlive. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ^ @NWSPittsburgh (August 25, 2023). "Our damage survey team in Fayette County has confirmed a tornado of at least EF-2 intensity. Winds greater than 110mph. More details forthcoming. #pawx #Pittsburgh" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ Gmiter, Tanda (2023-08-25). "5 dead, several injured, widespread damage after storms tear across Michigan". mlive. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ^ Wulfeck, Andrew; Sistek, Scott; Andrews, Hillary (2023-08-24). "5 dead, 700k lose power as Great Lakes slammed with tornadoes, 75 mph winds". Fox Weather. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- ^ "Q3 Global Catastrophe Recap October 2023" (PDF). Aon Benfield. Retrieved October 31, 2023.
- ^ "SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Saturday December 09, 2023". Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ a b Wesner Childs, Jan (December 9, 2023). "Tornadoes Cause Damage In Tennessee, Kentucky". The Weather Channel. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ Sistek, Scott; Barker, Aaron; Speck, Emilee (December 9, 2023). "Tornado outbreak leaves behind damage in Tennessee, Kentucky". FOX Weather. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "Clarksville sees severe tornado damage Saturday afternoon". News Channel 5 Nashville (WTVF). 2023-12-09. Retrieved 2023-12-09.
- ^ https://x.com/NWSLouisville/status/1733908875123064840?s=20
- ^ "Possible tornado touches down north of Clarksville; thousands without power". The Tennessean. Retrieved 2023-12-09.
- ^ Latham, Angele (December 9, 2023). "Damage from tornadoes, severe weather reported in Middle Tennessee". The Tennessean. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "Hendersonville Tornado Damage: Tennessee Twister Moving Fast, Gallatin And Goodlettsville Alerted | Video". TimesNow. 2023-12-10. Retrieved 2023-12-09.
- ^ "UPDATE: Death toll from Tennessee tornadoes rises to 6, including 3 in Clarksville and 3 in Nashville". X (formerly Twitter). December 9, 2023. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ "Confirmed casualties so far from the tornadoes in Tennessee:- Clarksville: 3 dead, 23 injured - Nashville: 3 dead (Madison area) - Hendersonville: Injuries reported". X (formerly Twitter). December 9, 2023. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- ^ Edmonds, Colbi; McGee, Jamie (December 10, 2023). "Six Dead and More Than 60 Injured After Severe Weather in Tennessee". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Saturday December 09, 2023". Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- ^ "'Tornado' hits Millicent with damage to houses, trees and power lines - ABC News". amp.abc.net.au. Retrieved 2023-12-13.
- ^ "Tornados e tempo severo nos dias 11 e 12 de julho de 2023" (in Portuguese). Prevots. 26 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "Cascavel registrou tornado nesta quarta (4), afirma Simepar; FOTOS". G1 (in Brazilian Portuguese). 2023-10-04. Retrieved 2023-10-07.